Switch from epoetin to darbepoetin alfa in hemodialysis: dose equivalence and hemoglobin stability
- PMID: 25336984
- PMCID: PMC4199978
- DOI: 10.2147/IJNRD.S61895
Switch from epoetin to darbepoetin alfa in hemodialysis: dose equivalence and hemoglobin stability
Abstract
Aim: The objective of the study reported here was to describe dose equivalence and hemoglobin (Hb) stability in a cohort of unselected hemodialysis patients who were switched simultaneously from epoetin alfa to darbepoetin alfa.
Methods: This was a multicenter, observational, retrospective study in patients aged ≥18 years who switched from intravenous (IV) epoetin alfa to IV darbepoetin alfa in October 2007 (Month 0) and continued on hemodialysis for at least 24 months. The dose was adjusted to maintain Hb within 1.0 g/dL of baseline.
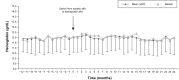
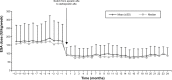
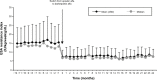
Results: We included 125 patients (59.7% male, mean [standard deviation (SD)] age 70.4 [13.4] years). No significant changes were observed in Hb levels (mean [SD] 11.9 [1.3] g/dL, 12.0 [1.5], 12.0 [1.5], and 12.0 [1.7] at Months -12, 0, 12 and 24, respectively, P=0.409). After conversion, the erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) dose decreased significantly (P<0.0001), with an annual mean of 174.7 (88.7) international units (IU)/kg/week for epoetin versus 95.7 (43.4) (first year) and 91.4 (42.7) IU/kg/week (second year) for darbepoetin (65% and 64% reduction, respectively). The ESA resistance index decreased from 15.1 (8.5) IU/kg/week/g/dL with epoetin to 8.1 (3.9) (first year) and 7.9 (4.0) (second year) with darbepoetin (P<0.0001). The conversion rate was 354:1 in patients requiring high (>200 IU/kg/week) doses of epoetin and 291:1 in patients requiring low doses.
Conclusion: In patients on hemodialysis receiving ESAs, conversion from epoetin alfa to darbepoetin alfa was associated with an approximate and persistent reduction of 65% of the required dose. To maintain Hb stability, a conversion rate of 300:1 seems to be appropriate for most patients receiving low doses of epoetin alfa (≤200 IU/kg/week), while 350:1 would be better for patients receiving higher doses.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; darbepoetin alfa; dose equivalence; epoetin alfa; hemodialysis; hemoglobin.
Figures
References
-
- Macdougall IC. Optimizing the use of erythropoietic agents – pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17(Suppl 5):66–70. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Aljama P, Bárány P, et al. European Best Practice Guidelines Working Group Revised European best practice guidelines for the management of anaemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19(Suppl 2):ii1–ii47. - PubMed
-
- Nissenson AR, Swan SK, Lindberg JS, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of darbepoetin alfa for the treatment of anemia in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40(1):110–118. - PubMed
-
- Fishbane S. The role of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in the treatment of anemia. Am J Manag Care. 2010;16(Suppl Issues):S67–S73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

