Assessment of air pockets in high-dose-rate vaginal cuff brachytherapy using cylindrical applicators
- PMID: 25337128
- PMCID: PMC4200182
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2014.45436
Assessment of air pockets in high-dose-rate vaginal cuff brachytherapy using cylindrical applicators
Abstract
Purpose: To retrospectively assess the incidence and magnitude of air pockets around vaginal cylinders and its impact on dose distribution in vaginal cuff image-guided high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy.
Material and methods: Fifty endometrial carcinoma patients treated by postoperative HDR vaginal cuff brachytherapy were included in the study. The average age of patients was 58.3 ± 11.8 years (range: 31-87 years). Brachytherapy was performed using cylindrical applicators, and the dose prescribed to 0.5 cm from the applicator's surface, over a length of 5 cm from the applicator's tip. Computed tomography (CT) simulation was used for each brachytherapy fraction. The incidence, vaginal mucosa displacement, volume, and dosimetric effect of air pockets around the vaginal cylinder were evaluated.
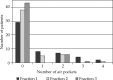
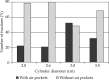
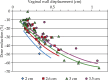
Results: A total of 78 air pockets were found in 29/50 patients (58%) and 45/135 (33%) brachytherapy plans. They were located at the apex: 16/78 (20%) and lateral to the applicator: 62/78 (80%). The volume of air pockets ranged between 0.01 and 2.1 cm(3) (mean: 0.15 cm(3) ± 0.36 cm(3)), and the maximum displacement of vaginal mucosa from cylinder surface was between 0.1 and 1.09 cm (mean: 0.34 cm ± 0.2 cm). The dose reduction to the vaginal mucosa generated by the air pockets ranged from 0.5 to 66% (mean: 26.4% ± 13.9%).
Conclusions: The presence of air pockets around vaginal cylinder applicators is frequently noticed in post-operative vaginal cuff brachytherapy. The dose to the vaginal mucosa is reduced, as a result of displacement generated by air pockets. The effect on the clinical outcome of this dose reduction is yet to be determined.
Keywords: air pockets; brachytherapy cylinder; endometrial carcinoma; vaginal brachytherapy.
Figures

References
-
- Horowitz NS, Peters WA, Smith MR, et al. Adjuvant high dose rate vaginal brachytherapy as treatment of stage I and II endometrial carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Pearcey RG, Petereit DG. Post-operative high dose rate brachytherapy in patients with low to intermediate risk endometrial cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2000;56:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Small W, Beriwal S, Demanes DJ, et al. American Brachytherapy Society consensus guidelines for adjuvant vaginal cuff brachytherapy after hysterectomy. Brachytherapy. 2012;11:58–67. - PubMed
-
- Choo JJ, Scudiere J, Bitterman P, et al. Vaginal lymphatic channel location and its implication for intracavitary brachytherapy radiation treatment. Brachytherapy. 2005;4:236–240. - PubMed
-
- Richardson S, Palaniswaamy G, Grigsby PW. Dosimetric effects of air pockets around high-dose-rate brachytherapy vaginal cylinders. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78:276–279. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
