High-dose-rate brachytherapy boost for prostate cancer: rationale and technique
- PMID: 25337138
- PMCID: PMC4200189
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2014.45759
High-dose-rate brachytherapy boost for prostate cancer: rationale and technique
Abstract
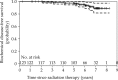
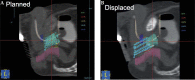
High-dose-rate brachytherapy (HDR) is a method of conformal dose escalation to the prostate. It can be used as a local boost in combination with external beam radiotherapy, with a high degree of efficacy and low rate of long term toxicity. Data consistently reports relapse free survival rates of greater than 90% for intermediate risk patients and greater than 80% for high risk. Results are superior to those achieved with external beam radiotherapy alone. A wide range of dose and fractionation is reported, however, we have found that a single 15 Gy HDR combined with hypofractionated radiotherapy to a dose of 37.5 Gy in 15 fractions is well tolerated and is associated with a long term relapse-free survival of over 90%. Either CT-based or trans-rectal ultrasound-based planning may be used. The latter enables treatment delivery without having to move the patient with risk of catheter displacement. We have found it to be an efficient and quick method of treatment, allowing catheter insertion, planning, and treatment delivery to be completed in less than 90 minutes. High-dose-rate boost should be considered the treatment of choice for many men with high and intermediate risk prostate cancer.
Keywords: HDR; boost; brachytherapy; external beam radiotherapy; intermediate risk; prostate cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High dose-rate brachytherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer.Transl Androl Urol. 2018 Jun;7(3):357-370. doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.12.08. Transl Androl Urol. 2018. PMID: 30050796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brachytherapy: current status and future strategies -- can high dose rate replace low dose rate and external beam radiotherapy?Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2013 Aug;25(8):474-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 30. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2013. PMID: 23727431 Review.
-
A combined single high-dose rate brachytherapy boost with hypofractionated external beam radiotherapy results in a high rate of biochemical disease free survival in localised intermediate and high risk prostate cancer patients.Radiother Oncol. 2016 Nov;121(2):299-303. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Radiother Oncol. 2016. PMID: 28029404 Clinical Trial.
-
Normal tissue dosimetric comparison between HDR prostate implant boost and conformal external beam radiotherapy boost: potential for dose escalation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000 Mar 1;46(4):851-8. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(99)00501-5. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000. PMID: 10705005
-
Results of multiparametric transrectal ultrasound-based focal high-dose-rate dose escalation combined with supplementary external beam irradiation in intermediate- and high-risk localized prostate cancer patients.Brachytherapy. 2017 Mar-Apr;16(2):277-281. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Brachytherapy. 2017. PMID: 27964906
Cited by
-
Phase I/IIa trial of androgen deprivation therapy, external beam radiotherapy, and stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for high-risk prostate cancer (ADEBAR).Radiat Oncol. 2020 Oct 8;15(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01665-6. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33032643 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PSA nadir predicts biochemical recurrence after external beam radiation therapy combined to high dose rate brachytherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2022 Feb 15;10(1):52-62. eCollection 2022. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2022. PMID: 35291420 Free PMC article.
-
High dose-rate brachytherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer.Transl Androl Urol. 2018 Jun;7(3):357-370. doi: 10.21037/tau.2017.12.08. Transl Androl Urol. 2018. PMID: 30050796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating Routine Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Planning for the Delivery of High-dose-rate Brachytherapy for Prostate Cancer: An Evaluation of Clinical Feasibility and Dosimetric Outcomes.Cureus. 2019 Feb 16;11(2):e4085. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4085. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31019863 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative Search for Circulating Tumor Cells in Patients Undergoing Prostate Brachytherapy for Clinically Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 11;18(1):128. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010128. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28085051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bentzen JK, Ockelmann HH, Hansen HS. High dose rate 192ir-microselectron. Ugeskr Laeger. 1990;152:2908–2910. [in Danish] - PubMed
-
- Mate TP, Gottesman JE, Hatton J, et al. High dose-rate afterloading 192Iridium prostate brachytherapy: feasibility report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;41:525–533. - PubMed
-
- Stromberg J, Martinez A, Gonzalez J, et al. Ultrasound-guided high dose rate conformal brachytherapy boost in prostate cancer: treatment description and preliminary results of a phase I/II clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33:161–171. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs G, Galalae R, Loch T, et al. Prostate preservation by combined external beam and HDR brachytherapy in nodal negative prostate cancer. Strahlenther Onkol. 1999;175(Suppl 2):87–88. - PubMed
-
- Kestin LL, Martinez AA, Stromberg JS, et al. Matched-pair analysis of conformal high-dose-rate brachytherapy boost versus external-beam radiation therapy alone for locally advanced prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2869–2880. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
