Identification, expression and phylogenetic analysis of EgG1Y162 from Echinococcus granulosus
- PMID: 25337206
- PMCID: PMC4203177
Identification, expression and phylogenetic analysis of EgG1Y162 from Echinococcus granulosus
Abstract
Objective: This study was to clone, identify and analyze the characteristics of egG1Y162 gene from Echinococcus granulosus.
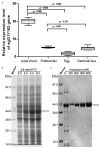
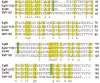
Methods: Genomic DNA and total RNAs were extracted from four different developmental stages of protoscolex, germinal layer, adult and egg of Echinococcus granulosus, respectively. Fluorescent quantitative PCR was used for analyzing the expression of egG1Y162 gene. Prokaryotic expression plasmid of pET41a-EgG1Y162 was constructed to express recombinant His-EgG1Y162 antigen. Western blot analysis was performed to detect antigenicity of EgG1Y162 antigen. Gene sequence, amino acid alignment and phylogenetic tree of EgG1Y162 were analyzed by BLAST, online Spidey and MEGA4 software, respectively.
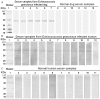
Results: EgG1Y162 gene was expressed in four developmental stages of Echinococcus granulosus. And, egG1Y162 gene expression was the highest in the adult stage, with the relative value of 19.526, significantly higher than other three stages. Additionally, Western blot analysis revealed that EgG1Y162 recombinant protein had good reaction with serum samples from Echinococcus granulosus infected human and dog. Moreover, EgG1Y162 antigen was phylogenetically closest to EmY162 antigen, with the similarity over 90%.
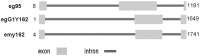
Conclusion: Our study identified EgG1Y162 antigen in Echinococcus granulosus for the first time. EgG1Y162 antigen had a high similarity with EmY162 antigen, with the genetic differences mainly existing in the intron region. And, EgG1Y162 recombinant protein showed good antigenicity.
Keywords: EgG1Y162 antigen; fluorescent quantitative PCR; phylogenetic tree; prokaryotic expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Cloning and sequence analysis of the egG1Y162 gene of Echinococcus granulosus].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2009 Apr;27(2):177-9. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19856513 Chinese.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of EgA31 and EgG1Y162 proteins for designing a multi-epitope vaccine against Echinococcus granulosus.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Sep;73:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 31022474
-
Immunization of mice with egG1Y162-1/2 provides protection against Echinococcus granulosus infection in BALB/c mice.Mol Immunol. 2018 Feb;94:183-189. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29328998
-
Bioinformatic features and immunological response of recombinant antigen CTLA4-IgV-EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Nov 25;57:e13139. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13139. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39607201 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant subunits as tools for the structural and functional characterization of Echinococcus granulosus antigen B.Exp Parasitol. 2008 Aug;119(4):490-498. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2008.04.015. Epub 2008 Apr 24. Exp Parasitol. 2008. PMID: 18513717 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of a Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Echinococcus granulosus in Immunoinformatics.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:668492. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668492. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34456902 Free PMC article.
-
Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162-EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus.Open Life Sci. 2023 Mar 14;18(1):20220558. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0558. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36941829 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-3/Galectin-9 signaling pathway is involved in the cytokine changes in mice with alveolar echinococcosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Aug;49(8):7497-7506. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07554-3. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35715604
-
Evaluation of protective immune responses induced by DNA vaccines encoding Echinococcus granulosus EgM123 protein in Beagle dogs.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 25;11:1444741. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1444741. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39386253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu JH. Border areas hydatid disease causes and prevention of epidemic response. Medical Information. 2007;20:682–3.
-
- Jiang CP. Current epidemic status of echinococcosis in chin. Endemic Diseases Bulletin. 2002;17:77–9.
-
- Wen H, Xu M. PracticaL echinococcosis. 1rd edition. Beijing: Science Publishing House; 2007. pp. 1–19.
-
- Katoh Y, Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Goto A, Suzuki T, Oku Y, Yagi K. Characterization of emY162 encoding an immunogenic protein cloned from an adult worm-specific cDNA library of Echinococcus multilocularis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1780:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
