Correlation of RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression in pathogenesis of gastric cancer
- PMID: 25337233
- PMCID: PMC4203204
Correlation of RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression in pathogenesis of gastric cancer
Abstract
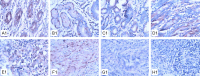
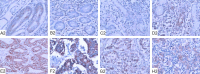
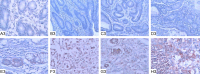
RKIP is proposed as a new metastasis suppressor. Our recent study showed that RKIP inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells. However, the underlying mechanism of RKIP function in gastric cancer is unclear. This study aimed to investigate the correlation of RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression in the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer. RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 proteins were detected by immunohistochemistry in tissues of gastric ulcer (n = 27), gastric adenomatous polyp (n = 7), intestinal metaplasia (n = 26), dysplasia (n = 40), gastric carcinoma (n = 169) and metastatic lymph node (n = 36). RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-PCR in SGC7901 cells. We found that RKIP protein expression was significantly decreased in advanced gastric cancer and metastatic lymph node tissues while cyclin D1 and STAT3 protein expression was markedly increased in severe dysplasia, gastric cancer and metastatic lymph node tissue (P < 0.01). RKIP expression in gastric cancer was negatively correlated with the invasion, TNM stage and lymphoid node metastasis (P < 0.01), while cyclin D1 and STAT3 expression was positively correlated with histological differentiation and lymphoid node metastasis (P < 0.01). RKIP protein level was negatively correlated with cyclin D1 and STAT3 protein level, while cyclin D1 protein level was positively correlated with STAT3 protein level in gastric cancer samples. Moreover, reconstitution of RKIP in SGC7901 gastric cancer cells led to reduced cyclin D1 and STAT3 mRNA levels. In conclusion, these data suggest that RKIP inhibits gastric cancer metastasis via the downregulation of its downstream target genes STAT3 and cyclin D1.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; STAT3; cyclin D1; raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP).
Figures

References
-
- Herszényi L, Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M. The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) in health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:1049–1053. - PubMed
-
- Zeng L, Imamoto A, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP): a physiological regulator and future therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12:1275–1287. - PubMed
-
- Granovsky AE, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein: a signal transduction modulator and metastasis suppressor. Cell Res. 2008;18:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Fu Z, Kitagawa Y, Shen R, Shah R, Mehra R, Rhodes D, Keller PJ, Mizokami A, Dunn R, Chinnaiyan AM, Yao Z, Keller ET. Metastasis suppressor gene Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) is a novel prognostic marker in prostate cancer. Prostate. 2006;66:248–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
