Increased expression of IRS-1 is associated with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 25337259
- PMCID: PMC4203230
Increased expression of IRS-1 is associated with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
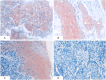
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a head and neck malignant tumor rare throughout most of the world but common in Southeast Asia, especially in Southern China, which is with characteristics of early cervical lymph node metastasis and high incidence rate of distant metastasis. Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) is a signaling adapter protein that is encoded by the IRS-1 gene in humans, plays an important role in the development, progression, invasion and metastasis of tumors. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between the expression of IRS-1 protein and clinicopathological characteristics in NPC by immunohistochemistry. The results showed that the expression level of IRS-1 was significant higher in NPC than that in the control nasopharyngeal epithelia (P = 0.042). The positive percentage of IRS-1 expression in NPC with lymph node metastasis was also significantly higher than those without lymph node metastasis (P = 0.008). Positive expression of IRS-1 was proved to be the independent predicted factor for lymph node metastasis of NPC (P = 0.025) regardless of age, gender, histological type and clinical stages by multivariate logistic regression analysis. In addition, results showed higher sensitivity and agreement rate of IRS-1 for predicting lymph node metastasis of NPC patients. Taken together, high expression of IRS-1 might be closely correlated with lymph node metastasis in NPC and positive expression of IRS-1 could be used as an independent biomarker for predicting lymph node metastasis of NPC.
Keywords: Insulin receptor substrate (IRS); biomarker; insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1); metastasis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylated Mnk1 and eIF4E are associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 14;9(2):e89220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089220. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551240 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of flotillin-2 protein as a novel biomarker for lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 11;9(7):e101676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101676. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25014228 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant SATB1 expression is associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection, metastasis and survival in human nasopharyngeal cells and endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2454-61. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966956 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 Expression in the Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Oncology. 2025;103(3):253-264. doi: 10.1159/000541004. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Oncology. 2025. PMID: 39186927
-
Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 is closely correlated with clinical outcome in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6099-105. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4464-1. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26611644
Cited by
-
Serum IRS-1 acts as a novel biomarker for diagnosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Jul 1;11(7):3685-3690. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949750 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous p53-R280T Mutation Enhances the Oncogenicity of NPC Cells Through Activating PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 5;10:104. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00104. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117754 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IGF1R pathway in cancer with microRNAs: How close are we?RNA Biol. 2018 Mar 4;15(3):320-326. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1338240. Epub 2018 Feb 1. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28613101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ΔNp63 in squamous cell carcinoma: defining the oncogenic routes affecting epigenetic landscape and tumour microenvironment.Mol Oncol. 2019 May;13(5):981-1001. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12473. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30845357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircTMTC1 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through targeting miR-495-MET-eIF4G1 translational regulation axis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Mar 18;13(3):250. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04686-z. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35301291 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
