IgG4-related renal disease: clinical and pathological characteristics
- PMID: 25337295
- PMCID: PMC4203266
IgG4-related renal disease: clinical and pathological characteristics
Abstract
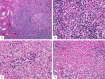
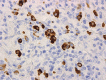
IgG4-related disease is a recently established systemic condition. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is the most common renal manifestation. Glomerular lesions, particularly membranous glomerulonephritis, can develop simultaneously. Some patients present with serological renal dysfunction associated with elevated IgG or IgE levels and hypocomplementemia, while others are incidentally found to have abnormalities in kidneys on imaging. A majority of patients with IgG4-related kidney disease have similar lesions at other anatomical sites, which help us to suspect this condition. Serum IgG4 elevation (>135 mg/dL) is the most, although not entirely, specific marker for the diagnosis. Imaging findings varies from small nodules to bilateral diffuse abnormalities. In addition to the renal parenchyma, the renal pelvis and perirenal adipose tissue can be affected. Histological features include dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, storiform or "bird's eye" fibrosis (highlighted by PAM stain), and IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration (>10 cells/high-power field and IgG4/IgG-positive cell ratio >40%). Immune complex deposition is detectable in the tubular basement membrane by immunofluorescence and/or electron microscopy. Patients usually respond well to corticosteroids, but highly active diseases may require other immunosuppressive therapies. Further investigations will be required to fully understand pathophysiology underlying this emerging condition.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; kidney; review.
Figures
References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, Kiyosawa K. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas-an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis. 1961;6:688–698. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida K, Toki T, Takeuchi T, Watanabe SI, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40:1561–1568. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N, Nakajima H. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–984. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Takahashi H, Imai K. Elevated IgG4 concentration in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33:432–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
