Intracerebroventricular injection of lipopolysaccharide increases gene expression of connexin32 gap junction in rat hippocampus
- PMID: 25337366
- PMCID: PMC4202574
Intracerebroventricular injection of lipopolysaccharide increases gene expression of connexin32 gap junction in rat hippocampus
Abstract
Introduction: Gap junctions are intercellular membrane channels that provide direct cytoplasmic continuity between adjacent cells. This communication can be affected by changes in expression of gap junctional subunits called Connexins (Cx). Changes in the expression and function of connexins are associated with number of brain neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroinflammation is a hallmark of various central nervous system (CNS) diseases, like multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy. Neuroinflammation causes change in Connexins expression. Hippocampus, one of the main brain regions with a wide network of Gap junctions between different neural cell types, has particular vulnerability to damage and consequent inflammation. Cx32 - among Connexins- is expressed in hippocampal Olygodandrocytes and some neural subpopulations. Although multiple lines of evidence indicate that there is an association between neuroinflammation and the expression of connexin, the direct effect of neuroinflammation on the expression of connexins has not been well studied. In the present study, the effect of neuroinflammation induced by the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on Cx32 gene and protein expressions in rat hippocampus is evaluated.
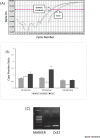
Methods: LPS (2.5µg/rat) was infused into the rat cerebral ventricles for 14 days. Cx32 mRNA and protein levels were measured by Real Time PCR and Western Blot after 1st, 7th and 14th injection of LPS in the hippocampus.
Results: Significant increase in Cx32 mRNA expression was observed after 7th injection of LPS (P < 0.001). However, no significant change was observed in Cx32 protein level.
Conclusion: LPS seems to modify Cx32 GJ communication in the hippocampus at transcription level but not at translation or post-translation level. In order to have a full view concerning modification of Cx32 GJ communication, effect of LPS on Cx32 channel gating should also be determined.
Keywords: Connexin32; Hippocampus; LPS; mRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., Brent, R., Kingston, R. E., et al. (2002). Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. (5th ed.). Wiley, New York
-
- Bennett, M.V.L. and Zukin, R.S. (2004). Electrical coupling and neuronal synchronization in the mammalian brain. Journal of Neuron. (41) 495–511 - PubMed
-
- Chanson, M., Derouette, J, P., Roth, I., Foglia, B., Scerri, I., Dudez, T., Kwak, B, R.. ( 2005). Gap junctional communication in tissue inflammation and repair. Biochim Biophys Acta, (1711)197–207 - PubMed
-
- Condorelli, D, F., Trovato-salinaro, A., Mudo, G., Mirone, M. B., Belluardo, N. (2003). Cellular expression of connexins in the rat brain: neuronal localization, effects of kainite-induced seizures and expression in apoptotic neuronal cells. Euro Journal of Neurosci. (18) 1807–27 - PubMed
-
- Cronin, M., Anderson, P. N., Cook, J. E., Green, C. R., Becker, D. L. (2008). Blocking connexin43 expression reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Journal of Mole and Cell Neurosci. (39) 152–160 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
