Kaempferol Downregulates Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor and ErbB3 Signaling in HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cells
- PMID: 25337585
- PMCID: PMC4189510
- DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2014.19.2.161
Kaempferol Downregulates Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor and ErbB3 Signaling in HT-29 Human Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background: Novel dietary agents for colon cancer prevention and therapy are desired. Kaempferol, a flavonol, has been reported to possess anticancer activity. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of the anticancer effects of kaempferol. The aim of this study was to determine the inhibitory effect of kaempferol on growth factor-induced proliferation and to elucidate its underlying mechanisms in the HT-29 human colon cancer cell line.
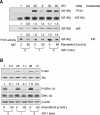
Methods: To assess the effects of kaempferol and/or growth factors [insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and heregulin (HRG)-β], cells were cultured with or without 60 μmol/L kaempferol and/or 10 nmol/L IGF-I or 20 μg/L HRG-β. Cell proliferation, DNA synthesis, and apoptosis were determined by a cell viability assay, a [(3)H]thymidine incorporation assay, and Annexin-V staining, respectively. Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and an in vitro kinase assay were conducted to evaluate expression and activation of various signaling molecules involved in the IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) and ErbB3 signaling pathways.
Results: IGF-I and HRG-β stimulated HT-29 cell growth but did not abrogate kaempferol-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. Kaempferol reduced IGF-II secretion, HRG expression and phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2. Kaempferol reduced IGF-I- and HRG-β-induced phosphorylation of the IGF-IR and ErbB3, their association with p85, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity. Additionally, kaempferol inhibited IGF-I- and HRG-β-induced phosphorylation of Akt and ERK-1/2.
Conclusions: The results demonstrate that kaempferol downregulates activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK-1/2 pathways by inhibiting IGF-IR and ErbB3 signaling in HT-29 cells. We suggest that kaempferol could be a useful chemopreventive agent against colon cancer.
Keywords: ErbB3; HT-29 human colon cancer; Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor; Kaempferol.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.BMC Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan 23;12:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22269172 Free PMC article.
-
Fucoidan downregulates insulin-like growth factor-I receptor levels in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1516-1522. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6193. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328495
-
Trans-10,cis-12, not cis-9,trans-11, conjugated linoleic acid decreases ErbB3 expression in HT-29 human colon cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 7;11(33):5142-50. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i33.5142. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16127743 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Phytonutrient Kaempferol in the Prevention of Gastrointestinal Cancers: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;16(9):1711. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091711. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol - A dietary anticancer molecule with multiple mechanisms of action: Recent trends and advancements.J Funct Foods. 2017 Mar;30:203-219. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.01.022. Epub 2017 Jan 18. J Funct Foods. 2017. PMID: 32288791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kaempferol Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Renal Cancer Cells through the Downregulation of AKT and FAK Pathways.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Aug 18;14(10):984-993. doi: 10.7150/ijms.20336. eCollection 2017. Int J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28924370 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Pharmacology Uncovers the Multiple Mechanisms of Xijiao Dihuang Decoction for the Treatment of Viral Hemorrhagic Fever.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:9025036. doi: 10.1155/2016/9025036. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27239215 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular docking and in vitro experiments verified that kaempferol induced apoptosis and inhibited human HepG2 cell proliferation by targeting BAX, CDK1, and JUN.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Apr;478(4):767-780. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04546-6. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36083512
-
Chemical Characterization of Sambucus nigra L. Flowers Aqueous Extract and Its Biological Implications.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 17;11(8):1222. doi: 10.3390/biom11081222. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439888 Free PMC article.
-
An Association Map on the Effect of Flavonoids on the Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2016 Apr 29;13(5):374-85. doi: 10.7150/ijms.14485. eCollection 2016. Int J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27226778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL, Leung WK. Asia Pacific Working Group on Colorectal Cancer. Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia: implications for screening. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:871–6. - PubMed
-
- Surh YJ. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:768–80. - PubMed
-
- Han X, Shen T, Lou H. Dietary polyphenols and their biological significance. Int J Mol Sci. 2007;8:950–88.
-
- Ross JA, Kasum CM. Dietary flavonoids: bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22:19–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
