Characteristic and functional analysis of a newly established porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line
- PMID: 25337908
- PMCID: PMC4206455
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110916
Characteristic and functional analysis of a newly established porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line
Abstract
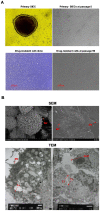
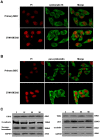
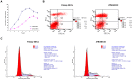
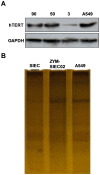
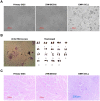
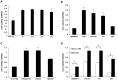
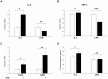
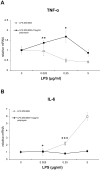
The mucosal surface of intestine is continuously exposed to both potential pathogens and beneficial commensal microorganisms. Recent findings suggest that intestinal epithelial cells, which once considered as a simple physical barrier, are a crucial cell lineage necessary for maintaining intestinal immune homeostasis. Therefore, establishing a stable and reliable intestinal epithelial cell line for future research on the mucosal immune system is necessary. In the present study, we established a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line (ZYM-SIEC02) by introducing the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene into small intestinal epithelial cells derived from a neonatal, unsuckled piglet. Morphological analysis revealed a homogeneous cobblestone-like morphology of the epithelial cell sheets. Ultrastructural indicated the presence of microvilli, tight junctions, and a glandular configuration typical of the small intestine. Furthermore, ZYM-SIEC02 cells expressed epithelial cell-specific markers including cytokeratin 18, pan-cytokeratin, sucrase-isomaltase, E-cadherin and ZO-1. Immortalized ZYM-SIEC02 cells remained diploid and were not transformed. In addition, we also examined the host cell response to Salmonella and LPS and verified the enhanced expression of mRNAs encoding IL-8 and TNF-α by infection with Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium). Results showed that IL-8 protein expression were upregulated following Salmonella invasion. TLR4, TLR6 and IL-6 mRNA expression were upregulated following stimulation with LPS, ZYM-SIEC02 cells were hyporeponsive to LPS with respect to IL-8 mRNA expression and secretion. TNFα mRNA levels were significantly decreased after LPS stimulation and TNF-α secretion were not detected challenged with S. Typhimurium neither nor LPS. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that ZYM-SIEC02 cells retained the morphological and functional characteristics typical of primary swine intestinal epithelial cells and thus provide a relevant in vitro model system for future studies on porcine small intestinal pathogen-host cell interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Burch DG (1982) Tiamulin feed premix in the prevention and control of swine dysentery under farm conditions in the UK. Vet Rec 110: 244–246. - PubMed
-
- Schierack P, Nordhoff M, Pollmann M, Weyrauch KD, Amasheh S, et al. (2006) Characterization of a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line for in vitro studies of microbial pathogenesis in swine. Histochem Cell Biol 125: 293–305. - PubMed
-
- Gibson-D'Ambrosio RE, Samuel M, D'Ambrosio SM (1986) A method for isolating large numbers of viable disaggregated cells from various human tissues for cell culture establishment. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 22: 529–534. - PubMed
-
- Panja A (2000) A novel method for the establishment of a pure population of nontransformed human intestinal primary epithelial cell (HIPEC) lines in long term culture. Lab Invest 80: 1473–1475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

