The level of circulating octanoate does not predict ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT)-mediated acylation of ghrelin during fasting
- PMID: 25337923
- PMCID: PMC4283022
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2014-1318
The level of circulating octanoate does not predict ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT)-mediated acylation of ghrelin during fasting
Abstract
Background: Acyl-ghrelin is a 28-amino acid peptide released from the stomach. Ghrelin O-acyl transferase (GOAT) attaches an 8-carbon medium-chain fatty acid (MCFA) (octanoate) to serine 3 of ghrelin. This acylation is necessary for the activity of ghrelin. Animal data suggest that MCFAs provide substrate for GOAT and an increase in nutritional octanoate increases acyl-ghrelin.
Objectives: To address the question of the source of substrate for acylation, we studied whether the decline in ghrelin acylation during fasting is associated with a decline in circulating MCFAs.
Methods: Eight healthy young men (aged 18-28 years, body mass index range, 20.6-26.2 kg/m(2)) had blood drawn every 10 minutes for acyl- and desacyl-ghrelin and every hour for free fatty acids (FFAs) during the last 24 hours of a 61.5-hour fast and during a fed day. FFAs were measured by a highly sensitive liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy method. Acyl- and desacyl-ghrelin were measured in an in-house assay; the results were published previously. Ghrelin acylation was assessed by the ratio of acyl-ghrelin to total ghrelin.
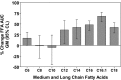
Results: With the exception of MCFAs C8 and C10, all other FFAs, the MCFAs (C6 and C12), and the long-chain fatty acids (C14-C18) significantly increased with fasting (P < .05). There was no significant association between the fold change in ghrelin acylation and circulating FFAs.
Conclusions: These results suggest that changes in circulating MCFAs are not linked to the decline in ghrelin acylation during fasting and support the hypothesis that acylation of ghrelin depends at least partially on the availability of gastroluminal MCFAs or the regulation of GOAT activity.
Figures
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–660. - PubMed
-
- Tschoep M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407:908–913. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Brown MS, Liang G, Grishin NV, Goldstein JL. Identification of the acyltransferase that octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone. Cell. 2008;132:387–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources