Functional improvement of regulatory T cells from rheumatoid arthritis subjects induced by capsular polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannogalactan
- PMID: 25338013
- PMCID: PMC4206502
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111163
Functional improvement of regulatory T cells from rheumatoid arthritis subjects induced by capsular polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannogalactan
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Functional Improvement of Regulatory T Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Subjects Induced by Capsular Polysaccharide Glucuronoxylomannogalactan.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 25;16(2):e0247971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247971. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33630956 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: Regulatory T cells (Treg) play a critical role in the prevention of autoimmunity, and the suppressive activity of these cells is impaired in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The aim of the present study was to investigate function and properties of Treg of RA patients in response to purified polysaccharide glucuronoxylomannogalactan (GXMGal).
Methods: Flow cytometry and western blot analysis were used to investigate the frequency, function and properties of Treg cells.
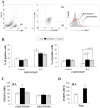
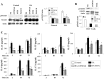
Results: GXMGal was able to: i) induce strong increase of FOXP3 on CD4+ T cells without affecting the number of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ Treg cells with parallel increase in the percentage of non-conventional CD4+CD25-FOXP3+ Treg cells; ii) increase intracellular levels of TGF-β1 in CD4+CD25-FOXP3+ Treg cells and of IL-10 in both CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ and CD4+CD25-FOXP3+ Treg cells; iii) enhance the suppressive activity of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ and CD4+CD25-FOXP3+ Treg cells in terms of inhibition of effector T cell activity and increased secretion of IL-10; iv) decrease Th1 response as demonstrated by inhibition of T-bet activation and down-regulation of IFN-γ and IL-12p70 production; v) decrease Th17 differentiation by down-regulating pSTAT3 activation and IL-17A, IL-23, IL-21, IL-22 and IL-6 production.
Conclusion: These data show that GXMGal improves Treg functions and increases the number and function of CD4+CD25-FOXP3+ Treg cells of RA patients. It is suggested that GXMGal may be potentially useful for restoring impaired Treg functions in autoimmune disorders and for developing Treg cell-based strategies for the treatment of these diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tim3+ Foxp3 + Treg Cells Are Potent Inhibitors of Effector T Cells and Are Suppressed in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Inflammation. 2017 Aug;40(4):1342-1350. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0577-6. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28478516
-
[Study on ratio imbalance of peripheral blood Th17/Treg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Mar;26(3):267-9, 272. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20230694 Chinese.
-
Phenotypic, Functional, and Gene Expression Profiling of Peripheral CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ CD4+CD25+CD127(low) Treg Cells in Patients With Chronic Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;68(1):103-16. doi: 10.1002/art.39408. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26314565 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune arthritis.Immunol Rev. 2010 Jan;233(1):97-111. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00848.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20192995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plasticity of human Treg and Th17 cells and its role in autoimmunity.Semin Immunol. 2013 Nov 15;25(4):305-12. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.10.009. Epub 2013 Nov 5. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24211039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered immunoregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of regulatory T cells and proinflammatory Th17 cells and therapeutic implications.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:751793. doi: 10.1155/2015/751793. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25918479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Augmenting regulatory T cells: new therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 23;15:1312919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1312919. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplantation of IL-1β siRNA-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates type II collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Feb;23(2):139. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.11062. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35069820 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Concern: Functional Improvement of Regulatory T Cells from Rheumatoid Arthritis Subjects Induced by Capsular Polysaccharide Glucuronoxylomannogalactan.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 25;16(2):e0247971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247971. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33630956 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen G, Zhang X, Li R, Fang L, Niu X, et al. (2010) Role of osteopontin in synovial Th17 differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62: 2900–2908. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Yang X, Zou H, Chu Y, Li M (2011) Recovery of the immune balance between Th17 and regulatory T cells as a treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50: 1366–1372. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Chu Y, Yang X, Gao D, Zhu L, et al. (2009) Th17 and natural Treg cell population dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60: 1472–1483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

