Evidence for α-helices in the large intracellular domain mediating modulation of the α1-glycine receptor by ethanol and Gβγ
- PMID: 25339760
- PMCID: PMC4279101
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.114.217976
Evidence for α-helices in the large intracellular domain mediating modulation of the α1-glycine receptor by ethanol and Gβγ
Erratum in
- J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Feb;352(2):325
Abstract
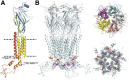
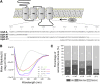
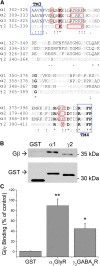
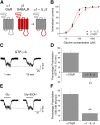
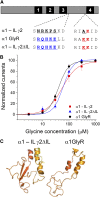
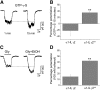
The α1-subunit containing glycine receptors (GlyRs) is potentiated by ethanol, in part, by intracellular Gβγ actions. Previous studies have suggested that molecular requirements in the large intracellular domain are involved; however, the lack of structural data about this region has made it difficult to describe a detailed mechanism. Using circular dichroism and molecular modeling, we generated a full model of the α1-GlyR, which includes the large intracellular domain and provides new information on structural requirements for allosteric modulation by ethanol and Gβγ. The data strongly suggest the existence of an α-helical conformation in the regions near transmembrane (TM)-3 and TM4 of the large intracellular domain. The secondary structure in the N-terminal region of the large intracellular domain near TM3 appeared critical for ethanol action, and this was tested using the homologous domain of the γ2-subunit of the GABAA receptor predicted to have little helical conformation. This region of γ2 was able to bind Gβγ and form a functional channel when combined with α1-GlyR, but it was not sensitive to ethanol. Mutations in the N- and C-terminal regions introduced to replace corresponding amino acids of the α1-GlyR sequence restored the ability to be modulated by ethanol and Gβγ. Recovery of the sensitivity to ethanol was associated with the existence of a helical conformation similar to α1-GlyR, thus being an essential secondary structural requirement for GlyR modulation by ethanol and G protein.
Copyright © 2014 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Aguayo LG, Pancetti FC. (1994) Ethanol modulation of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA- and glycine-activated Cl- current in cultured mouse neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Aguayo LG, Tapia JC, Pancetti FC. (1996) Potentiation of the glycine-activated Cl- current by ethanol in cultured mouse spinal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 279:1116–1122. - PubMed
-
- Bocquet N, Nury H, Baaden M, Le Poupon C, Changeux JP, Delarue M, Corringer PJ. (2009) X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation. Nature 457:111–114. - PubMed
-
- Bonacci TM, Ghosh M, Malik S, Smrcka AV. (2005) Regulatory interactions between the amino terminus of G-protein betagamma subunits and the catalytic domain of phospholipase Cbeta2. J Biol Chem 280:10174–10181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

