The HIV-1 gp120 CD4-bound conformation is preferentially targeted by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating antibodies in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals
- PMID: 25339767
- PMCID: PMC4301108
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02868-14
The HIV-1 gp120 CD4-bound conformation is preferentially targeted by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-mediating antibodies in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals
Abstract
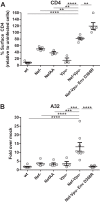
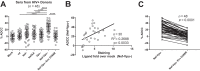
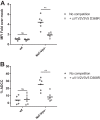
Recent studies have linked antibody Fc-mediated effector functions with protection or control of human immunodeficiency type 1 (HIV-1) and simian immunodeficiency (SIV) infections. Interestingly, the presence of antibodies with potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity in the Thai RV144 vaccine trial was suggested to correlate with decreased HIV-1 acquisition risk. These antibodies recently were found to recognize HIV envelope (Env) epitopes exposed upon Env-CD4 interaction. CD4 downregulation by Nef and Vpu, as well as Vpu-mediated BST-2 antagonism, were reported to modulate exposure of those CD4-induced HIV-1 Env epitopes and were proposed to play a role in reducing the susceptibility of infected cells to ADCC mediated by this class of antibodies. Here, we report the high prevalence of antibodies recognizing CD4-induced HIV-1 Env epitopes in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals, which correlated with their ability to mediate ADCC responses against HIV-1-infected cells, exposing these Env epitopes at the cell surface. Furthermore, our results indicate that Env variable regions V1, V2, V3, and V5 do not represent a major determinant for ADCC responses mediated by sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. Altogether, these findings suggest that HIV-1 tightly controls the exposure of certain Env epitopes at the surface of infected cells in order to prevent elimination by Fc-effector functions.
Importance: Here, we identified a particular conformation of HIV-1 Env that is specifically targeted by ADCC-mediating antibodies present in sera from HIV-1-infected individuals. This observation suggests that HIV-1 developed sophisticated mechanisms to minimize the exposure of these epitopes at the surface of infected cells.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

