Fifty Years of Family Planning: New Evidence on the Long-Run Effects of Increasing Access to Contraception
- PMID: 25339778
- PMCID: PMC4203450
- DOI: 10.1353/eca.2013.0001
Fifty Years of Family Planning: New Evidence on the Long-Run Effects of Increasing Access to Contraception
Abstract
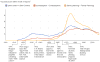
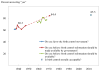
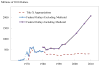
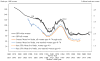
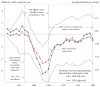
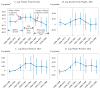
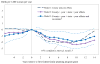
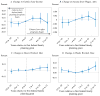
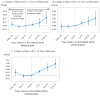
This paper assembles new evidence on some of the longer-term consequences of U.S. family planning policies, defined in this paper as those increasing legal or financial access to modern contraceptives. The analysis leverages two large policy changes that occurred during the 1960s and 1970s: first, the interaction of the birth control pill's introduction with Comstock-era restrictions on the sale of contraceptives and the repeal of these laws after Griswold v. Connecticut in 1965; and second, the expansion of federal funding for local family planning programs from 1964 to 1973. Building on previous research that demonstrates both policies' effects on fertility rates, I find suggestive evidence that individuals' access to contraceptives increased their children's college completion, labor force participation, wages, and family incomes decades later.
Figures


References
-
- Alan Guttmacher Institute. Fulfilling the Promise: Public Policy and US Family Planning Clinics. New York: 2000.
-
- Almond Douglas, Currie Janet. Human Capital Development before Age Five. In: Ashenfelter O, Card D, editors. Handbook of Labor Economics. 4b. Maryland Heights, Mo: Elsevier; 2011.
-
- Ananat Elizabeth, Gruber Jonathan, Levine Phillip, Staiger Douglas. Abortion and Selection. Review of Economics and Statistics. 2009;91(1):124–36.
-
- Bailey Beth L. Sex in the Heartland. Harvard University Press; 1999.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
