The contribution of cell surface FcRn in monoclonal antibody serum uptake from the intestine in suckling rat pups
- PMID: 25339905
- PMCID: PMC4188031
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00225
The contribution of cell surface FcRn in monoclonal antibody serum uptake from the intestine in suckling rat pups
Abstract
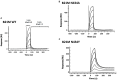
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) in intestinal epithelium is the primary mechanism for transfer of maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) from suckled milk to serum; but the factors contributing to the rapid uptake of IgG are poorly understood. These studies help to determine the contribution of cell surface FcRn in IgG uptake in 2-week-old rat pups by varying local pH and binding conditions. Variants of a human wild-type (WT) IgG monoclonal antibody (mAb WT) were assessed for binding affinity (KD) to rat (r)FcRn at pH 6.0 and subsequent off-rate at pH 7.4 (1/s) by surface plasmon resonance. Selected mAbs were administered intra-intestinally in isoflurane-anesthetized 2-week rat pups. Full length mAb in serum was quantified by immunoassay, (r)FcRn mRNA expression by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and mAb epithelial localization was visualized by immunohistochemistry. After duodenal administration, serum levels of mAb variants correlated with their rFcRn off-rate at pH 7.4, but not their affinity at pH 6.0. The greatest serum levels of IgG were measured when mAb was administered in the duodenum where rFcRn mRNA expression is greatest, and was increased further by duodenal administration in pH 6.0 buffer. More intense human IgG immunostaining was detected in epithelium than the same variant administered at higher pH. These data suggest an increased contribution for cell surface receptor. We conclude that, in the neonate duodenum, receptor off-rates are as important as affinities for FcRn mediated uptake, and cell surface binding of IgG to rFcRn plays contributes to IgG uptake alongside pinocytosis; both of which responsible for increased IgG uptake.
Keywords: FcRn; IgG; bioavailability; cell surface receptor; uptake.
Figures

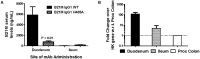
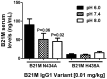

Similar articles
-
Contribution of FcRn binding to intestinal uptake of IgG in suckling rat pups and human FcRn-transgenic mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Feb 1;304(3):G262-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00340.2012. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23220220
-
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binds independently to both sites of the IgG homodimer with identical affinity.MAbs. 2015;7(2):331-43. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1008353. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25658443 Free PMC article.
-
Efflux of monoclonal antibodies from rat brain by neonatal Fc receptor, FcRn.Brain Res. 2013 Oct 9;1534:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23978455
-
Are endosomal trafficking parameters better targets for improving mAb pharmacokinetics than FcRn binding affinity?Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):660-74. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23917469 Review.
-
New functions of the MHC class I-related Fc receptor, FcRn.Biochem Soc Trans. 1997 May;25(2):481-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0250481. Biochem Soc Trans. 1997. PMID: 9191140 Review.
Cited by
-
Commentary: "There's been a Flaw in Our Thinking".Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 16;6:351. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00351. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26236309 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alternative Routes of Administration for Therapeutic Antibodies-State of the Art.Antibodies (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;11(3):56. doi: 10.3390/antib11030056. Antibodies (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36134952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fc-Engineering for Modulated Effector Functions-Improving Antibodies for Cancer Treatment.Antibodies (Basel). 2020 Nov 17;9(4):64. doi: 10.3390/antib9040064. Antibodies (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33212886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FcRn binding is not sufficient for achieving systemic therapeutic levels of immunoglobulin G after oral delivery of enteric-coated capsules in cynomolgus macaques.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016 Apr 25;4(3):e00218. doi: 10.1002/prp2.218. eCollection 2016 Jun. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016. PMID: 27433338 Free PMC article.
-
The pharmacology and therapeutic applications of monoclonal antibodies.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019 Dec;7(6):e00535. doi: 10.1002/prp2.535. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019. PMID: 31859459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berryman M., Rodewald R. (1995). Beta 2-microglobulin co-distributes with the heavy chain of the intestinal IgG-Fc receptor throughout the transepithelial transport pathway of the neonatal rat. J. Cell Sci. 108(Pt 6), 2347–2360 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

