Copy number variation in the horse genome
- PMID: 25340504
- PMCID: PMC4207638
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004712
Copy number variation in the horse genome
Abstract
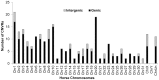
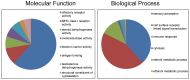
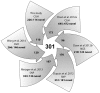
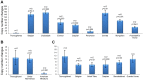
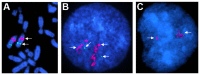
We constructed a 400K WG tiling oligoarray for the horse and applied it for the discovery of copy number variations (CNVs) in 38 normal horses of 16 diverse breeds, and the Przewalski horse. Probes on the array represented 18,763 autosomal and X-linked genes, and intergenic, sub-telomeric and chrY sequences. We identified 258 CNV regions (CNVRs) across all autosomes, chrX and chrUn, but not in chrY. CNVs comprised 1.3% of the horse genome with chr12 being most enriched. American Miniature horses had the highest and American Quarter Horses the lowest number of CNVs in relation to Thoroughbred reference. The Przewalski horse was similar to native ponies and draft breeds. The majority of CNVRs involved genes, while 20% were located in intergenic regions. Similar to previous studies in horses and other mammals, molecular functions of CNV-associated genes were predominantly in sensory perception, immunity and reproduction. The findings were integrated with previous studies to generate a composite genome-wide dataset of 1476 CNVRs. Of these, 301 CNVRs were shared between studies, while 1174 were novel and require further validation. Integrated data revealed that to date, 41 out of over 400 breeds of the domestic horse have been analyzed for CNVs, of which 11 new breeds were added in this study. Finally, the composite CNV dataset was applied in a pilot study for the discovery of CNVs in 6 horses with XY disorders of sexual development. A homozygous deletion involving AKR1C gene cluster in chr29 in two affected horses was considered possibly causative because of the known role of AKR1C genes in testicular androgen synthesis and sexual development. While the findings improve and integrate the knowledge of CNVs in horses, they also show that for effective discovery of variants of biomedical importance, more breeds and individuals need to be analyzed using comparable methodological approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inter- and intra-breed genome-wide copy number diversity in a large cohort of European equine breeds.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 22;20(1):759. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6141-z. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31640551 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide detection of copy number variations among diverse horse breeds by array CGH.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 30;9(1):e86860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086860. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24497987 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Detection of Copy Number Variants in Chinese Indigenous Horse Breeds and Verification of CNV-Overlapped Genes Related to Heat Adaptation of the Jinjiang Horse.Genes (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;13(4):603. doi: 10.3390/genes13040603. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456409 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Non-Coding Genome for the Diagnosis of Disorders of Sex Development.Sex Dev. 2021;15(5-6):392-410. doi: 10.1159/000519238. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Sex Dev. 2021. PMID: 34634785 Review.
-
Equine clinical genomics: A clinician's primer.Equine Vet J. 2010 Oct;42(7):658-70. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.2010.00166.x. Equine Vet J. 2010. PMID: 20840582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide detection of copy number variation in American mink using whole-genome sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2022 Sep 13;23(1):649. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08874-1. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36096727 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in copy number variation screening in herbivorous livestock genomes and their association with phenotypic traits.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jan 11;10:1334434. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1334434. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38274664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic diversity, evolution and selection in the major histocompatibility complex DRB and DQB loci in the family Equidae.BMC Genomics. 2020 Sep 30;21(1):677. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07089-6. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32998693 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of fine-scale recombination rate variation in the domestic horse.Genome Res. 2019 Oct;29(10):1744-1752. doi: 10.1101/gr.243311.118. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31434677 Free PMC article.
-
Resequencing of a Pekin duck breeding population provides insights into the genomic response to short-term artificial selection.Gigascience. 2023 Mar 20;12:giad016. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giad016. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Gigascience. 2023. PMID: 36971291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. New York: Springer-Verlag.150 pp.
-
- Iafrate AJ, Feuk L, Rivera MN, Listewnik ML, Donahoe PK, et al. (2004) Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat Genet 36: 949–951. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Jiang T, Mao JH, Balmain A, Peterson L, et al. (2004) Genomic segmental polymorphisms in inbred mouse strains. Nat Genet 36: 952–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

