Recovery from an acute infection in C. elegans requires the GATA transcription factor ELT-2
- PMID: 25340560
- PMCID: PMC4207467
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004609
Recovery from an acute infection in C. elegans requires the GATA transcription factor ELT-2
Erratum in
-
Correction: recovery from an acute infection in C. elegans requires the GATA transcription factor ELT-2.PLoS Genet. 2015 Apr 10;11(4):e1005100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005100. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25860400 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The mechanisms involved in the recognition of microbial pathogens and activation of the immune system have been extensively studied. However, the mechanisms involved in the recovery phase of an infection are incompletely characterized at both the cellular and physiological levels. Here, we establish a Caenorhabditis elegans-Salmonella enterica model of acute infection and antibiotic treatment for studying biological changes during the resolution phase of an infection. Using whole genome expression profiles of acutely infected animals, we found that genes that are markers of innate immunity are down-regulated upon recovery, while genes involved in xenobiotic detoxification, redox regulation, and cellular homeostasis are up-regulated. In silico analyses demonstrated that genes altered during recovery from infection were transcriptionally regulated by conserved transcription factors, including GATA/ELT-2, FOXO/DAF-16, and Nrf/SKN-1. Finally, we found that recovery from an acute bacterial infection is dependent on ELT-2 activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
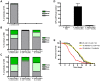
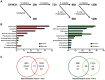
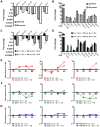
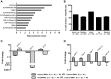
References
-
- Tenor JL, McCormick BA, Ausubel FM, Aballay A (2004) Caenorhabditis elegans-based screen identifies Salmonella virulence factors required for conserved host-pathogen interactions. Curr Biol 14: 1018–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

