Multiple regulatory systems coordinate DNA replication with cell growth in Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 25340815
- PMCID: PMC4207641
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004731
Multiple regulatory systems coordinate DNA replication with cell growth in Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
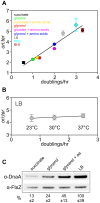
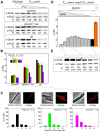
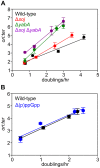
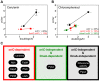
In many bacteria the rate of DNA replication is linked with cellular physiology to ensure that genome duplication is coordinated with growth. Nutrient-mediated growth rate control of DNA replication initiation has been appreciated for decades, however the mechanism(s) that connects these cell cycle activities has eluded understanding. In order to help address this fundamental question we have investigated regulation of DNA replication in the model organism Bacillus subtilis. Contrary to the prevailing view we find that changes in DnaA protein level are not sufficient to account for nutrient-mediated growth rate control of DNA replication initiation, although this regulation does require both DnaA and the endogenous replication origin. We go on to report connections between DNA replication and several essential cellular activities required for rapid bacterial growth, including respiration, central carbon metabolism, fatty acid synthesis, phospholipid synthesis, and protein synthesis. Unexpectedly, the results indicate that multiple regulatory systems are involved in coordinating DNA replication with cell physiology, with some of the regulatory systems targeting oriC while others act in a oriC-independent manner. We propose that distinct regulatory systems are utilized to control DNA replication in response to diverse physiological and chemical changes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of oriC relocation on control of replication initiation in Bacillus subtilis.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Sep;155(Pt 9):3070-3082. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.030080-0. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19574305
-
Rapid turnover of DnaA at replication origin regions contributes to initiation control of DNA replication.PLoS Genet. 2017 Feb 6;13(2):e1006561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006561. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28166228 Free PMC article.
-
DNA gyrase activity regulates DnaA-dependent replication initiation in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Apr;108(2):115-127. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13920. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29396913 Free PMC article.
-
How bacteria initiate DNA replication comes into focus.Bioessays. 2025 Jan;47(1):e2400151. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400151. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39390825 Review.
-
Regulating DNA replication in bacteria.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Apr 1;5(4):a012922. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012922. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23471435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The metabolic control of DNA replication: mechanism and function.Open Biol. 2023 Aug;13(8):230220. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230220. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37582405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism Shapes the Cell.J Bacteriol. 2017 May 9;199(11):e00039-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00039-17. Print 2017 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28320879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the Unwinding Region in the Clostridioides difficile Chromosomal Origin of Replication.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 2;11:581401. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.581401. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33133049 Free PMC article.
-
Growth rate and cell size: a re-examination of the growth law.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Apr;24:96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25662920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple mechanisms for overcoming lethal over-initiation of DNA replication.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Oct;118(4):426-442. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14976. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36053906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper S, Helmstetter CE (1968) Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol 31: 519–540. - PubMed
-
- Helmstetter CE, Cooper S (1968) DNA synthesis during the division cycle of rapidly growing Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol 31: 507–518. - PubMed
-
- Schaechter M, Maaloe O, Kjelgaard NO (1958) Dependency on medium and temperature on cell size and chemical coposition during balanced growth of Salmonella typhimurium . J Gen Microbiol 19: 592–606. - PubMed
-
- Donachie WD (1968) Relationship between cell size and time of initiation of DNA replication. Nature 219: 1077–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

