A Smoothened receptor agonist is neuroprotective and promotes regeneration after ischemic brain injury
- PMID: 25341035
- PMCID: PMC4649529
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.446
A Smoothened receptor agonist is neuroprotective and promotes regeneration after ischemic brain injury
Abstract
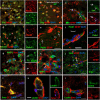
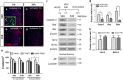
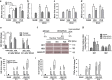
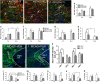
Ischemic stroke occurs as a result of blood supply interruption to the brain causing tissue degeneration, patient disabilities or death. Currently, treatment of ischemic stroke is limited to thrombolytic therapy with a narrow time window of administration. The sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway has a fundamental role in the central nervous system development, but its impact on neural cell survival and tissue regeneration/repair after ischemic stroke has not been well investigated. Here we report the neuroprotective properties of a small-molecule agonist of the Shh co-receptor Smoothened, purmorphamine (PUR), in the middle cerebral artery occlusion model of ischemic stroke. We found that intravenous administration of PUR at 6 h after injury was neuroprotective and restored neurological deficit after stroke. PUR promoted a transient upregulation of tissue-type plasminogen activator in injured neurons, which was associated with a reduction of apoptotic cell death in the ischemic cortex. We also observed a decrease in blood-brain barrier permeability after PUR treatment. At 14 d postinjury, attenuation of inflammation and reactive astrogliosis was found in PUR-treated animals. PUR increased the number of newly generated neurons in the peri-infarct and infarct area and promoted neovascularization in the ischemic zone. Notably, PUR treatment did not significantly alter the ischemia-induced level of Gli1, a Shh target gene of tumorigenic potential. Thus our study reports a novel pharmacological approach for postischemic treatment using a small-molecule Shh agonist, providing new insights into hedgehog signaling-mediated mechanisms of neuroprotection and regeneration after stroke.
Figures



References
-
- 1Shamy MC, Jaigobin CS. The complexities of acute stroke decision-making: a survey of neurologists. Neurology 2013; 81: 1130–1133. - PubMed
-
- 2Traiffort E, Angot E, Ruat M. Sonic Hedgehog signaling in the mammalian brain. J Neurochem 2010; 113: 576–590. - PubMed
-
- 3Charytoniuk D, Porcel B, Rodriguez Gomez J, Faure H, Ruat M, Traiffort E. Sonic Hedgehog signalling in the developing and adult brain. J Physiol Paris 2002; 96: 9–16. - PubMed
-
- 4Hynes M, Porter JA, Chiang C, Chang D, Tessier-Lavigne M, Beachy PA et al. Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron 1995; 15: 35–44. - PubMed
-
- 5Lu QR, Yuk D, Alberta JA, Zhu Z, Pawlitzky I, Chan J et al. Sonic hedgehog--regulated oligodendrocyte lineage genes encoding bHLH proteins in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuron 2000; 25: 317–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

