Level of adherence and HIV RNA suppression in the current era of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
- PMID: 25342151
- PMCID: PMC4393774
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-014-0927-4
Level of adherence and HIV RNA suppression in the current era of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
Abstract
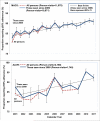
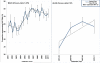
The need to achieve ≥95 % adherence to HAART for treatment effectiveness may be a barrier for universal initiation at early stages of HIV. Using longitudinal data collected from 2006 to 2011 from cohort studies of MSM (MACS) and IDUs (ALIVE study), we estimated the minimum adherence needed to achieve HIV RNA suppression (<50 copies/mL), defined as the level at which at least 80 % were virally suppressed, and the odds of suppression was not significantly different than that observed with ≥95 % adherence. In the MACS, ≥80 % suppression was observed with 80-84 % adherence and the odds ratio for suppression (vs. ≥95 % adherence) was 1.43 (0.61, 3.33). In the ALIVE study where <35 % were on newer drugs, only 71.4 % were suppressed among those who reported ≥95 % adherence. Although IDUs on older HAART regimens may need to be ≥95 % adherent, concerns related to non-adherence may be less of a barrier to initiation of modern HAART regimens.
Figures

References
-
- Global Health Observatory (GHO) [Jun 5, 2013];World Health Organization. Available at: http://www.who.int/gho/hiv/en/.
-
- Adeyemi OM, Badri SM, Max B, Chinomona N, Barker D. HIV infection in older patients. Clin. Infect Dis. 2003;36:1347. - PubMed
-
- Manfredi R. HIV infection and advanced age emerging epidemiological, clinical, and management issues. Ageing Research Reviews. 2004;3(1):31–54. - PubMed
-
- Deeks SG, Phillips AN. HIV infection, antiretroviral treatment, ageing, and non-AIDS related morbidity. BMJ. 2009;338:288–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036297/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA004334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA04334/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH058107/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI118591/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA12568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA012568/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1-AI35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

