Cdc48 and a ubiquitin ligase drive disassembly of the CMG helicase at the end of DNA replication
- PMID: 25342810
- PMCID: PMC4300516
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1253596
Cdc48 and a ubiquitin ligase drive disassembly of the CMG helicase at the end of DNA replication
Abstract
Chromosome replication is initiated by a universal mechanism in eukaryotic cells, involving the assembly and activation at replication origins of the CMG (Cdc45-MCM-GINS) DNA helicase, which is essential for the progression of replication forks. Disassembly of CMG is likely to be a key regulated step at the end of chromosome replication, but the mechanism was unknown until now. Here we show that the ubiquitin ligase known as SCF(Dia2) promotes ubiquitylation of CMG during the final stages of chromosome replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Cdc48/p97 segregase then associates with ubiquitylated CMG, leading rapidly to helicase disassembly. These findings indicate that the end of chromosome replication in eukaryotes is controlled in a similarly complex fashion to the much-better-characterized initiation step.
Copyright © 2014, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

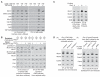

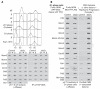
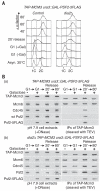
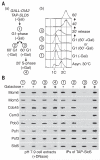
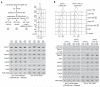
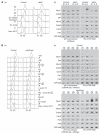
Comment in
-
DNA Replication. Terminating the replisome.Science. 2014 Oct 24;346(6208):418-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1261245. Science. 2014. PMID: 25342784 No abstract available.
-
Closing the MCM cycle at replication termination sites.EMBO Rep. 2014 Dec;15(12):1226-7. doi: 10.15252/embr.201439774. Epub 2014 Nov 12. EMBO Rep. 2014. PMID: 25391904 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gambus A, et al. GINS maintains association of Cdc45 with MCM in replisome progression complexes at eukaryotic DNA replication forks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006;8:358–366. doi:10.1038/ncb1382. - PubMed
-
- Boos D, Frigola J, Diffley JF. Activation of the replicative DNA helicase: Breaking up is hard to do. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012;24:423–430. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2012.01.011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

