Potent tumor targeting drug release system comprising MMP-2 specific peptide fragment with self-assembling characteristics
- PMID: 25342883
- PMCID: PMC4206202
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S67305
Potent tumor targeting drug release system comprising MMP-2 specific peptide fragment with self-assembling characteristics
Abstract
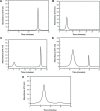
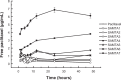
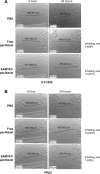
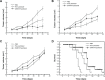
Self-assembling peptides are capable of forming a complex containing a cavity where cytotoxic agents can be wrapped in a self-assembling manner. These complexes are beneficial for improving the pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics of cytotoxic agents, such as doxorubicin and paclitaxel. In the present study, this self-assembling feature was successfully integrated into a hexapeptide with matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 specific targeting activity, producing a supramolecule possessing controlled drug release characteristics. The MMP-2 specific substrate fragment, PVGLIG, makes this supramolecule disassociate in the presence of MMP-2, and this system is considered to be a powerful tool for the treatment of tumors with high expression of MMP-2 or tumor metastasis. Our findings show that this modified self-assembling peptide with the PVGLIG fragment was able to significantly enhance specificity against HT1080 cells, a tumor cell line with high expression of MMP-2. In addition, residence time of the complex in blood was prolonged since paclitaxel was wrapped into the supramolecule. Our results suggest that the modified MMP-2 specific substrate, SAMTA7, could act as a controlled and sustained drug carrier for treatment of tumors with high expression of MMP-2 and for tumor metastasis.
Keywords: drug targeting system; matrix metalloproteinase; paclitaxel; self-assembly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted MMP-2 responsive chimeric polymersomes for therapy against colorectal cancer.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Sep;193:111135. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111135. Epub 2020 May 16. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 32447200
-
Controlled release strategy of paclitaxel by conjugating to matrix metalloproteinases-2 sensitive peptide.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):52230-52238. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10735. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27447567 Free PMC article.
-
Robust design of some selective matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibitors over matrix metalloproteinase-9 through in silico/fragment-based lead identification and de novo lead modification: Syntheses and biological assays.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Sep 15;24(18):4291-4309. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.07.023. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27452283
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Targeted Drug Delivery: Synthesis of a Potent and Highly Selective Inhibitor against Matrix Metalloproteinase- 7.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(27):2459-2471. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200722104928. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32703131 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 as a target for head and neck cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Feb;17(2):203-16. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.740012. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23252422 Review.
Cited by
-
(Macro)molecular self-assembly for hydrogel drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 May;172:275-295. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33450330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved Antiglioblastoma Activity and BBB Permeability by Conjugation of Paclitaxel to a Cell-Penetrative MMP-2-Cleavable Peptide.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020 Dec 21;8(3):2001960. doi: 10.1002/advs.202001960. eCollection 2021 Feb. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 33552853 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix-metalloproteinases as targets for controlled delivery in cancer: An analysis of upregulation and expression.J Control Release. 2017 Aug 10;259:62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.034. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28153760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact and mechanism of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs combined with chemotherapeutic drugs on human lung cancer-nude mouse transplanted tumors.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jun;11(6):4193-4199. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4493. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27313765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagedorn HG, Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG. Synthesis and degradation of basement membranes and extracellular matrix and their regulation by TGF-beta in invasive carcinomas (Review) Int J Oncol. 2001;18(4):669–681. - PubMed
-
- Mendes O, Kim HT, Lungu G, Stoica G. MMP-2 role in breast cancer brain metastasis development and its regulation by TIMP2 and ERK1/2. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007;24(5):341–351. - PubMed
-
- Kondratiev S, Gnepp DR, Yakirevich E, et al. Expression and prognostic role of MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP13, and MMP14 matrix metalloproteinases in sinonasal and oral malignant melanomas. Hum Pathol. 2008;39(3):337–343. - PubMed
-
- Zheng SQ, Huang RQ, Zhang YJ. Role of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9 and vascular endothelial growth factor C in lymph node metastasis of breast cancer. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2010;39(4):240–244. Chinese. - PubMed
-
- Negro A, Onisto M, Pellati D, Garbisa S. CNTF up-regulation of TIMP-2 in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997;48(1):30–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

