Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways
- PMID: 25342887
- PMCID: PMC4206205
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S71957
Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways
Abstract
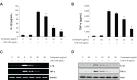
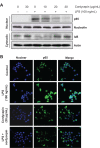
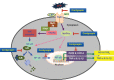
Cordycepin is the main functional component of the Cordyceps species, which has been widely used in traditional Oriental medicine. This compound possesses many pharmacological properties, such as an ability to enhance immune function, as well as antioxidant, antiaging, and anticancer effects. In the present study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin using a murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cell model. Our data demonstrated that cordycepin suppressed production of proinflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 by inhibiting inducible NO synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression. Cordycepin also inhibited the release of proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1-beta, through downregulation of respective mRNA expression. In addition, pretreatment with cordycepin significantly inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced phosphorylation of mitogen-activating protein kinases and attenuated nuclear translocation of NF-κB by LPS, which was associated with abrogation of inhibitor kappa B-alpha degradation. Furthermore, cordycepin potently inhibited the binding of LPS to macrophages and LPS-induced Toll-like receptor 4 and myeloid differentiation factor 88 expression. Taken together, the results suggest that the inhibitory effects of cordycepin on LPS-stimulated inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages are associated with suppression of mitogen-activating protein kinases and activation of NF-κB by inhibition of the Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB; Toll-like receptor 4; anti-inflammation; cordycepin; mitogen-activated protein kinases.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cordycepin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by the suppression of NF-kappaB through Akt and p38 inhibition in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 18;545(2-3):192-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.047. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16899239
-
Inhibitory effects of alternaramide on inflammatory mediator expression through TLR4-MyD88-mediated inhibition of NF-кB and MAPK pathway signaling in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 and BV2 cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Jan 25;244:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.11.024. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 26620692
-
Ganglioside GD1a suppresses LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines in RAW264.7 macrophages by reducing MAPKs and NF-κB signaling pathways through TLR4.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.044. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26054879
-
The Anticancer Properties of Cordycepin and Their Underlying Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 4;19(10):3027. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103027. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30287757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharides extracted from Lilium lancifolium Thunb.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Nov;52:119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.030. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28898768 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin K2 (MK-7) attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting inflammation, apoptosis, and ferroptosis.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 27;18(11):e0294763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294763. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38011192 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Launaea sarmentosa Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of NF-κB/MAPK Signaling and Nrf2 Activation.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 26;12(9):2586. doi: 10.3390/nu12092586. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32858855 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin protects against β-amyloid and ibotenic acid-induced hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neuronal hyperactivity.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;23(6):483-491. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2019.23.6.483. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31680770 Free PMC article.
-
Cordycepin Attenuates Testosterone-Induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Rats via Modulation of AMPK and AKT Activation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 8;14(8):1652. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081652. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015278 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lasia spinosa Leaf Extract in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 13;21(10):3439. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103439. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32414062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lind L. Circulating markers of inflammation and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2003;169(2):203–214. - PubMed
-
- Bertolini A, Ottani A, Sandrini M. Dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: a reappraisal. Pharmacol Res. 2001;44(6):437–450. - PubMed
-
- Kanno S, Shouji A, Tomizawa A, et al. Inhibitory effect of naringin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxin shock in mice and nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Life Sci. 2006;78(7):673–681. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282(5396):2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, et al. Bacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J. 1994;8(2):217–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

