Long-term outcome of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: impact of treatment and age
- PMID: 25342890
- PMCID: PMC4206251
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S64718
Long-term outcome of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: impact of treatment and age
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in operative repair, ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (rAAA) remains associated with high mortality and morbidity rates, especially in elderly patients. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of emergency endovascular aneurysm repair (eEVAR), conventional open repair (OPEN), and conservative treatment in elderly patients with rAAA.
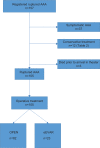
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of all rAAA patients treated with OPEN or eEVAR between January 2005 and December 2011 in the vascular surgery department at Amphia Hospital, the Netherlands. The outcome in patients treated for rAAA by eEVAR or OPEN repair was investigated. Special attention was paid to patients who were admitted and did not receive operative intervention due to serious comorbidity, extremely advanced age, or poor physical condition. We calculated the 30-day rAAA-related mortality for all rAAA patients admitted to our hospital.
Results: Twelve patients did not receive operative emergency repair due to extreme fragility (mean age 87 years, median time to mortality 27 hours). Twenty-three patients had eEVAR and 82 had OPEN surgery. The 30-day mortality rate in operated patients was 30% (7/23) in the eEVAR group versus 26% (21/82) in the OPEN group (P=0.64). No difference in mortality was noted between eEVAR and OPEN over 5 years of follow-up. There were more cardiac adverse events in the OPEN group (n=25, 31%) than in the eEVAR group (n=2, 9%; P=0.035). Reintervention after discharge was more frequent in patients who received eEVAR (35%) than in patients who had OPEN (6%, P<0.001). Advancing age was associated with increasing mortality (hazard ratio 1.05 [95% confidence interval 1.01-1.09]) per year for patients who received operative repair, with a 67%, 76%, and 100% 5-year mortality rate in the 34 patients aged <70 years, 59 patients aged 70-79 years, and 12 octogenarians, respectively; 30-day rAAA-related mortality was also associated with increasing age (21%, 30%, and 61%, respectively; P=0.008).
Conclusion: The 30-day and 5-year mortality in patients who survived rAAA was equal between the treatment options of eEVAR and OPEN. Particularly fragile and very elderly patients did not receive operative repair. The decision to intervene in rAAA should not be made on the basis of patient age alone, but also in relation to comorbidity and patient preference.
Keywords: clinical decision-making; emergency endovascular aneurysm repair; open repair; ruptured abdominal aneurysm repair.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mid-term outcomes following emergency endovascular aortic aneurysm repair for ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012 Apr;43(4):382-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2011.12.023. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22261485
-
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm: endovascular or open approach in a Dutch general hospital.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2011 Jun;52(3):363-9. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2011. PMID: 21577191
-
Endograft treatment of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms using the Talent aortouniiliac system: an international multicenter study.J Vasc Surg. 2006 Jun;43(6):1111-1123; discussion 1123. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.01.035. J Vasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 16765224
-
Systematic approach to ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm in the endovascular era: Intention-to-treat eEVAR protocol.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2012 Feb;53(1):77-82. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2012. PMID: 22231533 Review.
-
Outcome of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Repair in Octogenarians: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020 Jan;59(1):16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.07.014. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 31810836
Cited by
-
Short-term outcomes of endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm, including ruptured cases.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018 Jun;13(2):243-249. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2018.73358. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2018. PMID: 30002758 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative Treatment of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Vasc Specialist Int. 2023 Oct 31;39:32. doi: 10.5758/vsi.230073. Vasc Specialist Int. 2023. PMID: 37905386 Free PMC article.
-
The Comparison of Endovascular and Open Surgical Treatment for Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Terms of Safety and Efficacy on the Basis of a Single-Center 30-Year Experience.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 20;12(22):7186. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227186. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002798 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Outcomes After Open Repair for Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.World J Surg. 2020 Jun;44(6):2020-2027. doi: 10.1007/s00268-020-05457-7. World J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32152740 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency surgery in the elderly: challenges and solutions.Open Access Emerg Med. 2015 Sep 8;7:55-68. doi: 10.2147/OAEM.S68324. eCollection 2015. Open Access Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 27147891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Opfermann P, von Allmen R, Diehm N, Widmer MK, Schmidli J, Dick F. Repair of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm in octogenarians. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;42(4):475–483. - PubMed
-
- Hoornweg LL, Storm-Versloot MN, Ubbink DT, Koelemay MJ, Legemate DA, Balm R. Meta analysis on mortality of ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2008;35(5):558–570. - PubMed
-
- EVAR Trial Participants Endovascular aneurysm repair and outcome in patients unfit for open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm (EVAR trial 2): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9478):2187–2192. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf SW, Whitaker SC, Chuter TA, Wenham PW, Hopkinson BR. Emergency endovascular repair of leaking aortic aneurysm. Lancet. 1994;344(8937):1645. - PubMed
-
- Prusa AM, Wolff KS, Sahal M, et al. Abdominal aortic aneurysms and concomitant diseases requiring surgical intervention: simultaneous operation versus staged treatment using endoluminal stent grafting. Arch Surg. 2005;140(7):686–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

