Leakage evaluation of original and compatible implant-abutment connections: In vitro study using Rhodamine B
- PMID: 25342984
- PMCID: PMC4206669
- DOI: 10.1177/1758736014547143
Leakage evaluation of original and compatible implant-abutment connections: In vitro study using Rhodamine B
Abstract
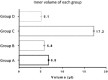
Leakage has been addressed as a major contributing factor to inflammatory reactions at the implant-abutment connection, leading to problems such as oral malodor, inflammation, and marginal bone loss. The aim of this study was to investigate in vitro the leakage at implant-abutment interface of OsseoSpeed™ implants connected to original and compatible abutments. A total of 28 OsseoSpeed implants were divided into four groups (n = 7). Each group was connected to four different abutments according to manufacturers' recommendations: group A (TiDesign™); group B (Natea™); group C (Dual™); and group D (Implanet™) abutments. The inner volume of each implant-abutment combination was calculated and leakage was detected for each group with spectrophotometric analysis at 1 h (D0) and 48 h (D1) of incubation time using Rhodamine B. At 1 h, leakage volume was significantly lower in TiDesign and Dual than in Natea and Implanet (P < 0.001). At 48 h, however, leakage was significantly lower between TiDesign and all other systems (P < 0.005). Compatible abutments do not fit internal connection of OsseoSpeed implants perfectly, which increases the leakage of the final assembly.
Keywords: Dental implants; Rhodamine B; abutment connection; compatible abutment; implant–abutment interface; leakage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, et al. . Marginal tissue reactions at osseointegrated titanium fixtures (I). A 3-year longitudinal prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1986; 15: 39–52 - PubMed
-
- Broggini N, McManus LM, Hermann JS, et al. . Persistent acute inflammation at the implant-abutment interface. J Dent Res 2003; 82: 232–237 - PubMed
-
- Broggini N, McManus LM, Hermann JS, et al. . Peri-implant inflammation defined by the implant-abutment interface. J Dent Res 2006; 85: 473–478 - PubMed
-
- Teixeira W, Ribeiro RF, Sato S, et al. . Microleakage into and from two-stage implants: an in vitro comparative study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2011; 26: 56–62 - PubMed
-
- Park SD, Lee Y, Kim YL, et al. . Microleakage of different sealing materials in access holes of internal connection implant systems. J Prosthet Dent 2012; 108: 173–180 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
