Leptin signaling
- PMID: 25343030
- PMCID: PMC4166933
- DOI: 10.12703/P6-73
Leptin signaling
Abstract
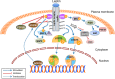
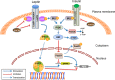
Leptin is secreted by adipose tissue and regulates energy homeostasis, glucose and lipid metabolism, immune function, and other systems. The binding of leptin to its specific receptor activates various intracellular signaling pathways, including Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/ signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), insulin receptor substrate (IRS)/phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 (SHP2)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/ acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Understanding of leptin signaling provides insights into its roles in health and disease.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

