Recent advances in the understanding of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 25343040
- PMCID: PMC4166934
- DOI: 10.12703/P6-83
Recent advances in the understanding of acute kidney injury
Abstract
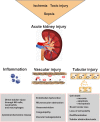
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical entity associated with high morbidity and mortality and clinical costs. The pathophysiology is multifaceted and involves inflammation, tubular injury, and vascular damage. Recently identified components include necroptosis, a special form of cell death, and autophagy. Most of the pathophysiological knowledge is obtained from animal models but these do not directly reflect the reality of the clinical situation. Tubular cells have a remarkable capacity to regenerate, and the role of stem/progenitor cells is discussed. Acute kidney injury is frequently associated with chronic kidney disease, and the implications are widespread.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Acute kidney injury: prevention, detection and management of acute kidney injury up to the point of renal replacement therapy; 2013 http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg169/resources/cg169-acute-kidney-injur...
-
- Gomez H, Ince C, Backer D de, Pickkers P, Payen D, Hotchkiss J, Kellum JA. A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury. Shock. 2014;41:3–11. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

