Classification and management of hepatolithiasis: A high-volume, single-center's experience
- PMID: 25343089
- PMCID: PMC4204570
- DOI: 10.5582/irdr.2012.v1.4.151
Classification and management of hepatolithiasis: A high-volume, single-center's experience
Abstract
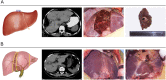
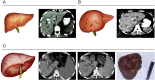
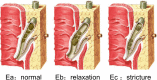
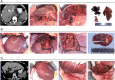
Hepatolithiasis is endemic to East Asia, but immigration from the region means that this rare but emerging disease will pose a therapeutic challenge to doctors in the West as well. Curative management of hepatolithiasis is difficult since its etiology has not been fully elucidated. Hepatectomy is the best approach to treating hepatolithiasis. Here, we propose a novel classification of hepatolithiasis and describe features of each type. We then relate our experience with various forms of hepatectomy to treat different types of hepatolithiasis. Surgery should be indicated for all cases of hepatolithiasis. The proposed classification will help to determine surgical strategies. Better selection of which patients should undergo a hepatectomy will lead to better outcomes.
Keywords: Hepatectomy; classification; hepatolithiasis.
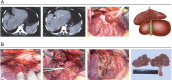
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgical management of hepatolithiasis.HPB (Oxford). 2009 May;11(3):194-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00046.x. HPB (Oxford). 2009. PMID: 19590647 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management of hepatolithiasis: A minireview.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2017 May;6(2):102-105. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2017.01027. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2017. PMID: 28580209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical therapy for hepatolithiasis: a Western experience.J Am Coll Surg. 2006 Feb;202(2):306-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.09.022. Epub 2005 Nov 21. J Am Coll Surg. 2006. PMID: 16427557
-
Indication and procedure for treatment of hepatolithiasis.Arch Surg. 2002 Feb;137(2):149-53. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.2.149. Arch Surg. 2002. PMID: 11822950
-
Liver transplantation for hepatolithiasis: Is terminal hepatolithiasis suitable for liver transplantation?Clin Transplant. 2016 Jun;30(6):651-8. doi: 10.1111/ctr.12731. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Clin Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26947018 Review.
Cited by
-
Nomogram predicting surgical risk of laparoscopic left-sided hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023 Sep 13;408(1):357. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-03099-6. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023. PMID: 37704787 Clinical Trial.
-
A Nomogram in Predicting Risks of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma After Partial Hepatectomy for Hepatolithiasis.J Gastrointest Surg. 2021 Sep;25(9):2258-2267. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-04947-w. Epub 2021 Feb 9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2021. PMID: 33565015
-
Clearing the Path: Redefining Hepatolithiasis Removal Through Endoscopic Hepaticogastrostomy.Cureus. 2025 Feb 9;17(2):e78775. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78775. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40070621 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical online nomogram for predicting prognosis in recurrent hepatolithiasis after biliary surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Feb 21;28(7):715-731. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i7.715. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35317276 Free PMC article.
-
Cholangiocarcinoma: novel therapeutic targets.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Apr;24(4):345-357. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1733528. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32077341 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kayhan B, Akdogan M, Parlak E, Ozarslan E, Sahin B. Hepatolithiasis: A Turkey experience. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2007; 18:28-32 - PubMed
-
- Park HS, Lee JM, Kim SH, Jeong JY, Kim YJ, Lee KH, Choi SH, Han JK, Choi BI. CT Differentiation of cholangiocarcinoma from periductal fibrosis in patients with hepatolithiasis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:445-453 - PubMed
-
- Mori T, Sugiyama M, Atomi Y. Gallstone disease: Management of intrahepatic stones. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 20:1117-1137 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
