A simple way to measure the burden of interval cancers in breast cancer screening
- PMID: 25344115
- PMCID: PMC4219107
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-782
A simple way to measure the burden of interval cancers in breast cancer screening
Abstract
Background: The sensitivity of a mammography program is normally evaluated by comparing the interval cancer rate to the expected breast cancer incidence without screening, i.e. the proportional interval cancer rate (PICR). The expected breast cancer incidence in absence of screening is, however, difficult to estimate when a program has been running for some time. As an alternative to the PICR we propose the interval cancer ratio ICR=intervalcancersintervalcancers+screendetectedcancers. We validated this simple measure by comparing it with the traditionally used PICR.
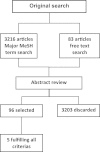
Method: We undertook a systematic review and included studies: 1) covering a service screening program, 2) women aged 50-69 years, 3) observed data, 4) interval cancers, women screened, or interval cancer rate, screen detected cases, or screen detection rate, and 5) estimated breast cancer incidence rate of background population. This resulted in 5 papers describing 12 mammography screening programs.
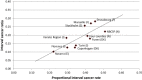
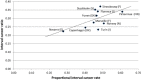
Results: Covering initial screens only, the ICR varied from 0.10 to 0.28 while the PICR varied from 0.22 to 0.51. For subsequent screens only, the ICR varied from 0.22 to 0.37 and the PICR from 0.28 to 0.51. There was a strong positive correlation between the ICR and the PICR for initial screens (r = 0.81), but less so for subsequent screens (r = 0.65).
Conclusion: This alternate measure seems to capture the burden of interval cancers just as well as the traditional PICR, without need for the increasingly difficult estimation of background incidence, making it a more accessible tool when evaluating mammography screening program performance.
Figures
References
-
- Mammography screening evaluation group HSCHC Mammography screening for breast cancer in Copenhagen April 1991-March1997. APMIS. 1998;106(suppl 83):1–44. - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/782/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

