Overcoming acquired resistance to cetuximab by dual targeting HER family receptors with antibody-based therapy
- PMID: 25344208
- PMCID: PMC4283113
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-242
Overcoming acquired resistance to cetuximab by dual targeting HER family receptors with antibody-based therapy
Abstract
Background: Cetuximab, an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, is used to treat several cancers. However, many patients who initially respond to cetuximab acquire resistance. To examine mechanisms of acquired resistance, we developed a series of cetuximab-resistant (Ctx(R)) clones derived from the cetuximab sensitive (CtxS) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line H226. Previous studies characterizing this model revealed that: 1) EGFR was robustly overexpressed in Ctx(R) clones due to decreased EGFR ubiquitination and degradation and 2) Ctx(R) clones expressed increased HER2 and HER3 activation resulting in constitutive activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling axis. These findings suggest that dual targeting HER family receptors would be highly beneficial in the Ctx(R) setting.
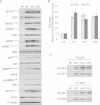
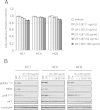
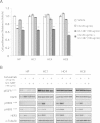
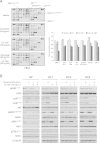
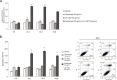
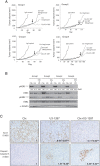
Results: Since HER3 has been implicated in resistance to EGFR inhibitors, the efficacy of dually targeting both EGFR and HER3 in Ctx(R) models was evaluated. First, EGFR and HER3 expression were knocked down with siRNAs. Compared to the Ctx(S) parental cell line (HP), all Ctx(R) clones exhibited robust decreases in cell proliferation upon dual knockdown. Analysis of Ctx(R) clones indicated that neuregulin-1 was highly overexpressed compared to HP cells. Incubation of HP cells with neuregulin-1 rendered them resistant to cetuximab. Next, dual treatment of Ctx(R) clones with cetuximab and the HER3 neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb) U3-1287 led to potent anti-proliferative effects. Blockade of EGFR with cetuximab resulted in inactivation of MAPK, while blockade of HER3 with U3-1287 resulted in the inactivation of AKT. Treatment with both mAbs resulted in knockdown of both signaling pathways simultaneously. HER2 was also strongly inactivated upon dual mAb therapy, suggesting that this treatment regimen can diminish signaling from three HER family receptors. De novo CtxR H226 mouse xenografts were established to determine if dual therapy could overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab in vivo. Tumors that had acquired resistance to cetuximab were significantly growth delayed upon dual treatment of U3-1287 and cetuximab compared to those continued on cetuximab only. Combinatorial-treated xenograft tumors expressed decreased Ki67 and increased cleaved caspase-3 levels compared to tumors treated with either monotherapy.
Conclusions: These studies demonstrate that dually targeting HER family receptors with antibody-based therapies can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sym004, a novel EGFR antibody mixture, can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab.Neoplasia. 2013 Oct;15(10):1196-206. doi: 10.1593/neo.131584. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 24204198 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib is a viable treatment for tumors with acquired resistance to cetuximab.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Sep 1;12(5):436-46. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.5.16394. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21725209 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the HER Family with Pan-HER Effectively Overcomes Resistance to Cetuximab.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Sep;15(9):2175-86. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0012. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27422810 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the pseudokinase HER3 in the acquired resistance against EGFR- and HER2-directed targeted therapy.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):831-6. doi: 10.1042/BST20140043. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25109965 Review.
-
Targeting of erbB3 receptor to overcome resistance in cancer treatment.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 8;13:105. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-105. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24886126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of heregulins, HER3, and HER4 as potential therapeutic targets in cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(51):89284-89306. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18467. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Tumor-Derived Matrix Improves the Predictability of Head and Neck Cancer Drug Testing.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 30;12(1):92. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010092. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31905951 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin Signaling Is a Mechanism of Therapeutic Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Nov;18(11):2124-2134. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0163. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31387891 Free PMC article.
-
Design and selection of optimal ErbB-targeting bispecific antibodies in pancreatic cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1168444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168444. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153618 Free PMC article.
-
HER3 protein expression in relation to HER2 positivity in patients with primary colorectal cancer: clinical relevance and prognostic value.Virchows Arch. 2015 Jun;466(6):645-54. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1747-2. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Virchows Arch. 2015. PMID: 25739551
References
-
- Maurizi M, Almadori G, Ferrandina G, Distefano M, Romanini ME, Cadoni G, Benedetti-Panici P, Paludetti G, Scambia G, Mancuso S. Prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1996;74:1253–1257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

