Harnessing the fcμ receptor for potent and selective cytotoxic therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 25344228
- PMCID: PMC4268434
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2030
Harnessing the fcμ receptor for potent and selective cytotoxic therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
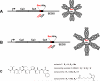
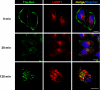
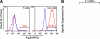
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a B-cell malignancy in need of new, effective, and safe therapies. The recently identified IgM receptor FcμR is overexpressed on malignant B cells in CLL and mediates the rapid internalization and lysosomal shuttling of IgM via its Fc fragment (Fcμ). To exploit this internalization and trafficking pathway for targeted drug delivery, we engineered an IgM-derived protein scaffold (Fcμ) and linked it with the cytotoxic agent monomethylauristatin F. This Fcμ-drug conjugate was selectively toxic for FcμR-expressing cell lines in vitro and for CLL cells but not autologous normal T cells ex vivo. Notably, the cytotoxic activity of the Fcμ-drug conjugate was maintained in CLL cells carrying a 17p deletion, which predicts resistance to standard chemotherapy. Next, we tested the possible therapeutic application of the Fcμ-drug conjugate in immunodeficient NOD/SCID/IL-2Rγ(null) (NSG) mice engrafted with peripheral blood cells from patients with leukemia. Three intravenous injections of the Fcμ-drug conjugate over a 10-day period were well tolerated and selectively killed the human CLL cells but not the coengrafted autologous human T cells. In summary, we developed a novel strategy for targeted cytotoxic therapy of CLL based on the unique properties of FcμR. FcμR-targeted drug delivery showed potent and specific therapeutic activity in CLL, thus providing proof of concept for FcμR as a valuable therapeutic target in CLL and for IgM-based antibody-drug conjugates as a new targeting platform.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
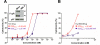

Similar articles
-
TOSO, the Fcmicro receptor, is highly expressed on chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells, internalizes upon IgM binding, shuttles to the lysosome, and is downregulated in response to TLR activation.J Immunol. 2011 Oct 15;187(8):4040-50. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100532. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21908732 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting Fc μ receptor selectively eliminate CLL cells while sparing healthy B cells.Blood. 2016 Sep 29;128(13):1711-22. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-692046. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27535994
-
Identity of the elusive IgM Fc receptor (FcmuR) in humans.J Exp Med. 2009 Nov 23;206(12):2779-93. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091107. Epub 2009 Oct 26. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19858324 Free PMC article.
-
The long elusive IgM Fc receptor, FcμR.J Clin Immunol. 2014 Jul;34 Suppl 1(0 1):S35-45. doi: 10.1007/s10875-014-0022-7. Epub 2014 May 3. J Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24793544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the IgM Fc Receptor in Immunity and Tolerance.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 22;10:529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00529. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30967868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin M perception by FcμR.Nature. 2023 Mar;615(7954):907-912. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05835-w. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Nature. 2023. PMID: 36949194
-
TOPK is highly expressed in circulating tumor cells, enabling metastasis of prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 May 20;6(14):12392-404. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3630. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25881543 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of reagents for selenocysteine conjugation and the stability of selenocysteine adducts.Org Biomol Chem. 2016 Jun 14;14(22):5141-7. doi: 10.1039/c6ob00775a. Epub 2016 May 17. Org Biomol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27184239 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum IgM and all-cause mortality risk in Chinese centenarians: a prospective cohort study.Immun Ageing. 2024 Oct 16;21(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00475-8. Immun Ageing. 2024. PMID: 39415263 Free PMC article.
-
Stable and Potent Selenomab-Drug Conjugates.Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Apr 20;24(4):433-442.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.02.012. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Cell Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28330604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adair JR, Howard PW, Hartley JA, Williams DG, Chester KA. Antibody-drug conjugates - a perfect synergy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12:1191–206. - PubMed
-
- Sievers EL, Senter PD. Antibody-drug conjugates in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:15–29. - PubMed
-
- de Claro RA, McGinn K, Kwitkowski V, Bullock J, Khandelwal A, Habtemariam B, et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval summary: brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma or relapsed systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:5845–9. - PubMed
-
- Baron JM, Boster BL, Barnett CM. Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1): a novel antibody-drug conjugate for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Senter PD, Sievers EL. The discovery and development of brentuximab vedotin for use in relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30:631–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

