Uptake of amino acids and their metabolic conversion into the compatible solute proline confers osmoprotection to Bacillus subtilis
- PMID: 25344233
- PMCID: PMC4272716
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02797-14
Uptake of amino acids and their metabolic conversion into the compatible solute proline confers osmoprotection to Bacillus subtilis
Abstract
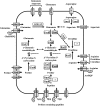
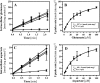
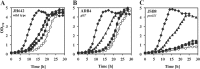
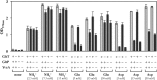
The data presented here reveal a new facet of the physiological adjustment processes through which Bacillus subtilis can derive osmostress protection. We found that the import of proteogenic (Glu, Gln, Asp, Asn, and Arg) and of nonproteogenic (Orn and Cit) amino acids and their metabolic conversion into proline enhances growth under otherwise osmotically unfavorable conditions. Osmoprotection by amino acids depends on the functioning of the ProJ-ProA-ProH enzymes, but different entry points into this biosynthetic route are used by different amino acids to finally yield the compatible solute proline. Glu, Gln, Asp, and Asn are used to replenish the cellular pool of glutamate, the precursor for proline production, whereas Arg, Orn, and Cit are converted into γ-glutamic semialdehyde/Δ(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, an intermediate in proline biosynthesis. The import of Glu, Gln, Asp, Asn, Arg, Orn, and Cit did not lead to a further increase in the size of the proline pool that is already present in osmotically stressed cells. Hence, our data suggest that osmoprotection of B. subtilis by this group of amino acids rests on the savings in biosynthetic building blocks and energy that would otherwise have to be devoted either to the synthesis of the proline precursor glutamate or of proline itself. Since glutamate is the direct biosynthetic precursor for proline, we studied its uptake and found that GltT, an Na(+)-coupled symporter, is the main uptake system for both glutamate and aspartate in B. subtilis. Collectively, our data show how effectively B. subtilis can exploit environmental resources to derive osmotic-stress protection through physiological means.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
L-Proline Synthesis Mutants of Bacillus subtilis Overcome Osmotic Sensitivity by Genetically Adapting L-Arginine Metabolism.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 16;13:908304. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.908304. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35783388 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of the compatible solute proline by Bacillus subtilis: point mutations rendering the osmotically controlled proHJ promoter hyperactive.Environ Microbiol. 2017 Sep;19(9):3700-3720. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13870. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28752945
-
Osmoprotection of Bacillus subtilis through import and proteolysis of proline-containing peptides.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Jan;79(2):576-87. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01934-12. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23144141 Free PMC article.
-
Guardians in a stressful world: the Opu family of compatible solute transporters from Bacillus subtilis.Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 1;398(2):193-214. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2016-0265. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27935846 Review.
-
Evolution of proline biosynthesis: enzymology, bioinformatics, genetics, and transcriptional regulation.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015 Nov;90(4):1065-99. doi: 10.1111/brv.12146. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015. PMID: 25367752 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic rewiring enables ammonium assimilation via a non-canonical fumarate-based pathway.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;17(3):e14429. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14429. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38483038 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Proline in Pathogen and Host Interactions.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Feb 1;30(4):683-709. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7335. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 29241353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essentiality of c-di-AMP in Bacillus subtilis: Bypassing mutations converge in potassium and glutamate homeostasis.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jan 22;17(1):e1009092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009092. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33481774 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced activation of the proline biosynthetic pathway in Bacillus subtilis: a population-wide and single-cell study of the osmotically controlled proHJ promoter.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;15(9):2411-2425. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14073. Epub 2022 May 20. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35593133 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of Four Putative δ1-Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Reductases from Bacillus subtilis.Front Microbiol. 2017 Aug 2;8:1442. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01442. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28824574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Logan N, De Vos P. 2009. Bacillus, p 21–128. In De Vos P, Garrity GM, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W, Rainey FR, Schleifer K-H, Whitman WB (ed), Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 3 Springer, Heidelberg, Germany.
-
- Barbe V, Cruveiller S, Kunst F, Lenoble P, Meurice G, Sekowska A, Vallenet D, Wang T, Moszer I, Medigue C, Danchin A. 2009. From a consortium sequence to a unified sequence: the Bacillus subtilis 168 reference genome a decade later. Microbiology 155:1758–1775. doi:10.1099/mic.0.027839-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

