Alemtuzumab: a new therapy for active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 25344374
- PMCID: PMC4361497
- DOI: 10.1177/1352458514549398
Alemtuzumab: a new therapy for active relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Abstract
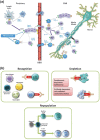
Alemtuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against CD52 to deplete circulating T and B lymphocytes; lymphocyte depletion is followed by a distinctive pattern of T- and B-cell repopulation, changing the balance of the immune system. This review reports the efficacy and safety findings of the phase 2 CAMMS223 trial and the phase 3 CARE-MS I and II trials investigating alemtuzumab for the treatment of active relapsing-remitting MS. Alemtuzumab, administered intravenously, was shown to improve relapse rate versus subcutaneous interferon beta-1a in patients who were treatment-naive (CAMMS223 and CARE-MS I) or had relapsed on prior therapy (CARE-MS II), and to reduce sustained accumulation of disability (CAMMS223 and CARE-MS II). Important adverse events were infusion-associated reactions, serious infections and autoimmune events. A safety monitoring program allowed for early detection and management of autoimmune events. Recommendations for the monitoring of adverse events are made. Alemtuzumab's mechanism of action, pharmacodynamics and opportunities for future research are discussed.
Keywords: Alemtuzumab; CD52; monoclonal antibody; multiple sclerosis.
© The Author(s), 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

