Ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rb1 attenuate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats
- PMID: 25344394
- PMCID: PMC4216840
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-415
Ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rb1 attenuate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats
Abstract
Background: Ginsenosides, the major bioactive compounds in ginseng root, have been found to have antioxidant, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities. This study investigated the effects of ginsenosides on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatitis and liver fibrosis in rats.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, CCl4, CCl4 + 0.5 g/kg Panax ginseng extract and CCl4 + 0.05 g/kg ginsenoside Rb1 groups. The treated groups were orally given Panax ginseng extract or ginsenoside Rb1 two weeks before the induction of liver injury for successive 9 weeks. Liver injury was induced by intraperitoneally injected with 400 ml/l CCl4 at a dose of 0.75 ml/kg body weight weekly for 7 weeks. The control group was intraperitoneally injected with olive oil.
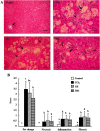
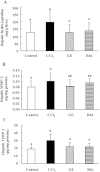
Results: The pathological results showed that ginsenoside Rb1 decreased hepatic fat deposition (2.65 ± 0.82 vs 3.50 ± 0.75, p <0.05) and Panax ginseng extract lowered hepatic reticular fiber accumulation (1.05 ± 0.44 vs 1.60 ± 0.39, p <0.01) increased by CCl4. Plasma alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase activities were increased by CCl4 (p <0.01), and aspartate aminotransferase activity was decreased by Panax ginseng extract at week 9 (p <0.05). Exposure to CCl4 for 7 weeks, the levels of plasma and hepatic triglycerides (p <0.01), hepatic cholesterol (p <0.01), interleukin-1β (p <0.01), prostaglandin E2 (p <0.05), soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (p <0.05), hydroxyproline (p <0.05), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (p <0.05) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) (p <0.01) were elevated, however, hepatic interleukin-10 level was lowered (p <0.05). Both Panax ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rb1 decreased plasma and hepatic triglyceride, hepatic prostaglandin E2, hydroxyproline and TIMP-1 levels, and Panax ginseng extract further inhibited interleukin-1β concentrations (p <0.05).
Conclusions: Panax ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rb1 attenuate plasma aminotransferase activities and liver inflammation to inhibit CCl4-induced liver fibrosis through down-regulation of hepatic prostaglandin E2 and TIMP-1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of ginseng extract on the TGF-β1 signaling pathway in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 13;17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1507-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28086769 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba, Panax ginseng, and Schizandra chinensis extract on liver injury in rats.Am J Chin Med. 2007;35(6):995-1009. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X07005466. Am J Chin Med. 2007. PMID: 18186586
-
Hepatoprotective activity of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng adventitious roots against carbon tetrachloride treated hepatic injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Dec 2;158 Pt A:442-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.047. Epub 2014 Oct 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25446594
-
Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 13;10(3):444. doi: 10.3390/biom10030444. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32183094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hepatoprotective Effects of Ginsenoside from Ginseng: A Review of Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potentials.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(7):957-971. doi: 10.2174/0113892010291326240214095327. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38424417 Review.
Cited by
-
Changbai Mountain Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Mey) Extract Supplementation Improves Exercise Performance and Energy Utilization and Decreases Fatigue-Associated Parameters in Mice.Molecules. 2017 Feb 5;22(2):237. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020237. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28165424 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Plants Compounds as Modulators of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 30;10:715. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00715. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31417401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Research on Active Compounds Against Hepatic Fibrosis.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(18):2571-2628. doi: 10.2174/0929867331666230727102016. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37497688 Review.
-
Ginsenosides: potential therapeutic source for fibrosis-associated human diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2020 May;44(3):386-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.12.003. Epub 2019 Dec 17. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32372860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of ginsenoside Rb1-imprinted magnetic polymer nanoparticles for the extraction and cellular delivery of therapeutic ginsenosides.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Sep;46(5):621-627. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.01.005. Epub 2022 Feb 4. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 36090682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neubauer K, Saile B, Ramadori G. Liver fibrosis and altered matrix synthesis. Can J Gastroenterol. 2001;15(3):187–193. - PubMed
-
- Lu SN, Su WW, Yang SS, Chang TT, Cheng KS, Wu JC, Lin HH, Wu SS, Lee CM, Changchien CS, Chen CJ, Sheu JC, Chen DS, Chen CH. Secular trends and geographic variations of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in Taiwan. Int J Cancer. 2006;119(8):1946–1952. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22045. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/14/415/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

