Generation of a neuro-specific microarray reveals novel differentially expressed noncoding RNAs in mouse models for neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 25344396
- PMCID: PMC4238357
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.047225.114
Generation of a neuro-specific microarray reveals novel differentially expressed noncoding RNAs in mouse models for neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
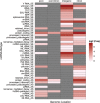
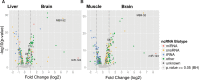
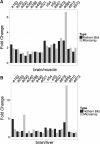
We have generated a novel, neuro-specific ncRNA microarray, covering 1472 ncRNA species, to investigate their expression in different mouse models for central nervous system diseases. Thereby, we analyzed ncRNA expression in two mouse models with impaired calcium channel activity, implicated in Epilepsy or Parkinson's disease, respectively, as well as in a mouse model mimicking pathophysiological aspects of Alzheimer's disease. We identified well over a hundred differentially expressed ncRNAs, either from known classes of ncRNAs, such as miRNAs or snoRNAs or which represented entirely novel ncRNA species. Several differentially expressed ncRNAs in the calcium channel mouse models were assigned as miRNAs and target genes involved in calcium signaling, thus suggesting feedback regulation of miRNAs by calcium signaling. In the Alzheimer mouse model, we identified two snoRNAs, whose expression was deregulated prior to amyloid plaque formation. Interestingly, the presence of snoRNAs could be detected in cerebral spine fluid samples in humans, thus potentially serving as early diagnostic markers for Alzheimer's disease. In addition to known ncRNAs species, we also identified 63 differentially expressed, entirely novel ncRNA candidates, located in intronic or intergenic regions of the mouse genome, genomic locations, which previously have been shown to harbor the majority of functional ncRNAs.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Parkinson's disease; microarray; noncoding RNAs; snoRNA; voltage-gated Ca2+ channels.
© 2014 Gstir et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures



References
-
- Bachellerie JP, Cavaille J, Huttenhofer A 2002. The expanding snoRNA world. Biochimie 84: 775–790. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B (Methodol) 57: 289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
