senX3-independent contribution of regX3 to Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence
- PMID: 25344463
- PMCID: PMC4213456
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-014-0265-8
senX3-independent contribution of regX3 to Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence
Abstract
Background: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) must adapt to various stress conditions during host infection. The two-component regulatory system (2CRS) SenX3-RegX3 is required for Mtb virulence. We showed recently that the senX3-regX3 intergenic region contains promoter activity, driving senX3-independent regX3 expression. In the current study, we tested the hypothesis that RegX3 has a SenX3-independent role in Mtb virulence. The gene expression patterns, growth, and survival of mutants containing transposon insertions in senX3 (senX3::Tn) and regX3 (regX3::Tn) were compared to those of their respective complemented strains and the isogenic wild-type parent strain during axenic growth in nutrient-rich broth, phosphate depletion, nutrient starvation, and in the lungs of BALB/c mice.
Results: regX3 expression was reduced in senX3::Tn during phosphate depletion and nutrient starvation, and expression of the phosphate-specific transport gene pstC2 was reduced similarly in senX3::Tn and regX3::Tn during phosphate depletion. Although senX3 and regX3 were each dispensable for Mtb growth in nutrient-rich broth, disruption of senX3 or regX3 caused a similar growth defect during phosphate depletion. Interestingly, senX3::Tn, in which monocistronic regX3 expression is preserved, showed significantly higher survival relative to regX3::Tn after 7 days of nutrient starvation (p <0.01), and in mouse lungs at Day 31 (p < 0.01), Day 62 (p < 0.01), and Day 124 (p = 0.05) after aerosol infection.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate the specificity of the senX3-regX3 2CRS for sensing and responding to low ambient phosphate, but also raise the possibility that RegX3 may function independently of its cognate sensor histidine kinase.
Figures
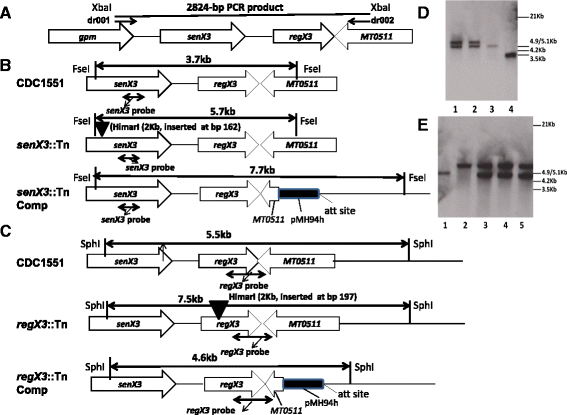
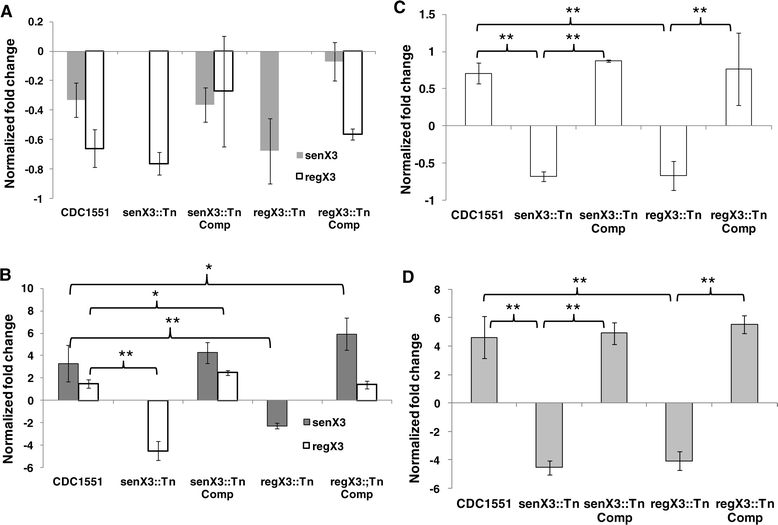

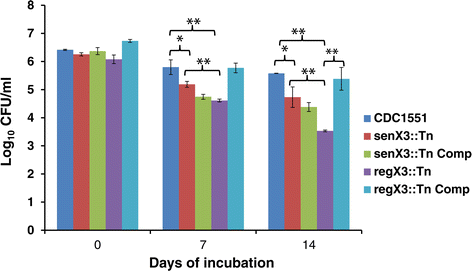


References
-
- Converse PJ, Karakousis PC, Klinkenberg LG, Kesavan AK, Ly LH, Allen SS, Grosset JH, Jain SK, Lamichhane G, Manabe YC, McMurray DN, Nuermberger EL, Bishai WR. Role of the dosR-dosS two-component regulatory system in mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence in three animal models. Infect Immun. 2009;77(3):1230–1237. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01117-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bagchi, Mayuri G, Das TK, Tyagi JS. Molecular analysis of the dormancy response in Mycobacterium smegmatis: expression analysis of genes encoding the DevR-DevS two-component system, Rv3134c and chaperone alpha-crystallin homologues. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002;211(2):231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

