T cell-B cell thymic cross-talk: maintenance and function of thymic B cells requires cognate CD40-CD40 ligand interaction
- PMID: 25344473
- PMCID: PMC4239311
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401655
T cell-B cell thymic cross-talk: maintenance and function of thymic B cells requires cognate CD40-CD40 ligand interaction
Abstract
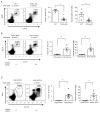
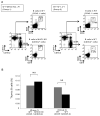
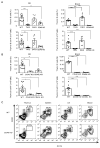
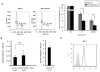
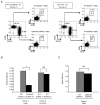
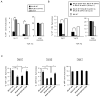
Thymic development requires bidirectional interaction or cross-talk between developing T cells and thymic stromal cells, a relationship that has been best characterized for the interaction between thymocytes and thymic epithelial cells. We have characterized in this article the requirement for similar cross-talk in the maintenance and function of thymic B cells, another population that plays a role in selection of developing thymic T cells. We found that maintenance of thymic B cells is strongly dependent on the presence of mature single-positive thymocytes and on the interactions of these T cells with specific Ag ligand. Maintenance of thymic B cell number is strongly dependent on B cell-autonomous expression of CD40, but not MHC class II, indicating that direct engagement of CD40 on thymic B cells is necessary to support their maintenance and proliferation. Thymic B cells can mediate negative selection of superantigen-specific, self-reactive, single-positive thymocytes, and we show that CD40 expression on B cells is critical for this negative selection. Cross-talk with thymic T cells is thus required to support the thymic B cell population through a pathway that requires cell-autonomous expression of CD40, and that reciprocally functions in negative selection of autoreactive T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD40 ligand functions non-cell autonomously to promote deletion of self-reactive thymocytes.J Immunol. 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2759-65. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2759. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11884443
-
Developmentally regulated availability of RANKL and CD40 ligand reveals distinct mechanisms of fetal and adult cross-talk in the thymus medulla.J Immunol. 2012 Dec 15;189(12):5519-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201815. Epub 2012 Nov 14. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23152561 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and phenotypic analysis of thymic B cells: role in the induction of T cell negative selection.Eur J Immunol. 1999 May;29(5):1598-609. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199905)29:05<1598::AID-IMMU1598>3.0.CO;2-O. Eur J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10359114
-
CD28-CD80/86 and CD40-CD40L Interactions Promote Thymic Tolerance by Regulating Medullary Epithelial Cell and Thymocyte Development.Crit Rev Immunol. 2015;35(1):59-76. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2015012501. Crit Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25746048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of CD40 and Its Ligand, gp39 (CD40L).Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):371-420. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.100. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773027 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-Associated Decline in Thymic B Cell Expression of Aire and Aire-Dependent Self-Antigens.Cell Rep. 2018 Jan 30;22(5):1276-1287. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.015. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29386114 Free PMC article.
-
The thymoproteasome hardwires the TCR repertoire of CD8+ T cells in the cortex independent of negative selection.J Exp Med. 2021 Apr 5;218(4):e20201904. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201904. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 33555295 Free PMC article.
-
Concepts for agonistic targeting of CD40 in immuno-oncology.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020;16(2):377-387. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1653744. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31403344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are activated B cells involved in the process of myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial infarction? An in vivo experiment.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Jan 6;21(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01775-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33407160 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperactivation and in situ recruitment of inflammatory Vδ2 T cells contributes to disease pathogenesis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 23;5:14432. doi: 10.1038/srep14432. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26395317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bohme J, Schuhbaur B, Kanagawa O, Benoist C, Mathis D. MHC-linked protection from diabetes dissociated from clonal deletion of T cells. Science. 1990;249:293–295. - PubMed
-
- Doffinger R, Klein TC, Pepys MB, Casanova JL, Kyewski BA. The MHC class II-restricted T cell response of C57BL/6 mice to human C-reactive protein: homology to self and the selection of T cell epitopes and T cell receptors. Molecular immunology. 1997;34:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Klein L, Kyewski B. “Promiscuous” expression of tissue antigens in the thymus: a key to T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity? J Mol Med (Berl) 2000;78:483–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

