Small molecule inhibitor YM155-mediated activation of death receptor 5 is crucial for chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma
- PMID: 25344582
- PMCID: PMC4387779
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0229
Small molecule inhibitor YM155-mediated activation of death receptor 5 is crucial for chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma
Abstract
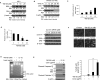
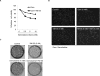
Despite much effort, pancreatic cancer survival rates are still dismally low. Novel therapeutics may hold the key to improving survival. YM155 is a small molecule inhibitor that has shown antitumor activity in a number of cancers by reducing the expression of survivin. The aim of our study is to understand the mechanisms by which YM155 functions in pancreatic cancer cells. We established the antitumor effect of YM155 with in vitro studies in cultured cells, and in vivo studies using a mouse xenograft model. Our data demonstrated that YM155 reduced the expression of survivin; however, downregulation of survivin itself is insufficient to induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. We showed for the first time that treatment with YM155 increased death receptor 5 (DR5) expression in pancreatic cancer cells. We found that YM155 induced apoptosis by broad-spectrum inhibition of IAP family member proteins (e.g., CIAP1/2 and FLIP) and induced proapoptotic Bak protein upregulation and activation; the antitumor effect of YM155 treatment with either the DR5 agonist lexatumumab or gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cells was synergistic. Our data also revealed that YM155 inhibits tumor growth in vivo, without apparent toxicity to the noncancerous human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line. Together, these findings suggest that YM155 could be a novel therapeutic agent for pancreatic cancer.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors disclose no conflicts
Figures




References
-
- Pavlidis TE, Psarras K, Symeonidis NG, Pavlidis ET, Sakantamis AK. Current surgical management of pancreatic endocrine tumor liver metastases. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011;10:243–7. - PubMed
-
- Castellanos EH, Cardin DB, Berlin JD. Treatment of early-stage pancreatic cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2011;25:182–9. - PubMed
-
- Paulson AS, Tran Cao HS, Tempero MA, Lowy AM. Therapeutic advances in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1316–26. - PubMed
-
- Pennarun B, Meijer A, de Vries EG, Kleibeuker JH, Kruyt F, de JS. Playing the DISC: turning on TRAIL death receptor-mediated apoptosis in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:123–40. - PubMed
-
- Schulze-Bergkamen H, Weinmann A, Moehler M, Siebler J, Galle PR. Novel ways to sensitise gastrointestinal cancer to apoptosis. Gut. 2009;58:1010–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

