FTY720 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma by inactivating STAT3 signaling
- PMID: 25344679
- PMCID: PMC4221672
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-783
FTY720 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cholangiocarcinoma by inactivating STAT3 signaling
Abstract
Background: Interleukin 6 (IL-6)-mediated signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT-3) phosphorylation (activation) is aberrantly sustained in cholangiocarcinoma cells resulting in enhanced myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1) expression and resistance to apoptosis. FTY720, a new immunosuppressant, derived from ISP-1, has been studied for its putative anti-cancer properties. This study aimed to elucidate the mechanism by which FTY720 mediates antitumor effects in cholangiocarcinoma (CC) cells.
Methods: Three CC cell lines were examined, QBC939, TFK-1, and HuCCT1. The therapeutic effects of FTY720 were evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, invasive potential, and epithelial- mesenchy-mal transition (EMT) were examined.
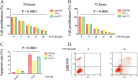
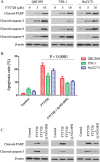
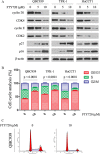
Results: FTY720 greatly inhibited CC cells proliferation and EMT in vitro and in vivo, and this effect was associated with dephosphorylation of STAT3tyr705. FTY720 induced apoptosis and G1 phase arrest in CC cells, and inhibited invasion of CC cells. Western blot analysis showed that FTY720 induced cleavage of caspases 3, 8 and 9, and of PARP, in a dose-dependent manner, consistent with a substantial decrease in p-STAT3, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, survivin, cyclin D1, cyclin E, N-cadherin, vimentin, VEGF and TWIST1. In vivo studies showed that tumor growth and metastasis were significantly suppressed after FTY720 treatment.
Conclusions: These results suggest that FTY720 induces a significant decrease in p-STAT3, which inhibits proliferation and EMT of CC cells, and then induces G1 phase arrest and apoptosis. We have characterized a novel immunosuppressant, which shows potential anti-tumor effects on CC via p-STAT3 inhibition. FTY720 merits further investigation and warrants clinical evaluation.
Figures



References
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/783/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

