Addition of bevacizumab enhances antitumor activity of erlotinib against non-small cell lung cancer xenografts depending on VEGF expression
- PMID: 25344762
- PMCID: PMC4236614
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-014-2610-x
Addition of bevacizumab enhances antitumor activity of erlotinib against non-small cell lung cancer xenografts depending on VEGF expression
Abstract
Purpose: Erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), and bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agent, are promising therapies for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Our study was aimed to determine whether there were conditions under which the addition of bevacizumab would enhance the antitumor activity of erlotinib against NSCLC tumors in vitro and in vivo.
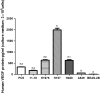
Methods: MTS was for NSCLC cell (PC9, 11-18, H1975, H157, H460 and A549) growth assay in vitro. ELISA was for VEGF protein assay in cells and tumor tissues. Mouse xenograft models were established with H157, H460 and A549 with primary resistance to erlotinib and treated with erlotinib plus bevacizumab or each agent alone. Erlotinib concentrations in tumors were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography.
Results: Bevacizumab alone did not inhibit NSCLC cell growth in vitro. In primarily erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells, the levels of VEGF protein were highest in H157 cell followed in order by H460 and A549 cells. In vivo, bevacizumab alone significantly inhibited tumor growth only in xenograft models with high (H157) and/or moderate (H460) levels of VEGF protein. A combination of erlotinib and bevacizumab partially reversed resistance to erlotinib in H157 xenografts (high VEGF level) with increasing intratumoral erlotinib concentrations, but not in H460 (moderate) or A549 (low) xenografts.
Conclusions: These results support that combined with anti-VEGF therapy could enhance antitumor activity of anti-EGFR therapy and/or partially reverse resistance to EGFR TKI, by increasing EGFR TKI concentration in specific tumors that express high levels of VEGF protein.
Figures




References
-
- Gerber DE. Targeted therapies: a new generation of cancer treatments. Am Fam Physician. 2008;77(3):311–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

