Physiological functions of MTA family of proteins
- PMID: 25344801
- PMCID: PMC4245464
- DOI: 10.1007/s10555-014-9514-4
Physiological functions of MTA family of proteins
Abstract
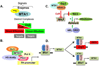
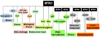
Although the functional significance of the metastasic tumor antigen (MTA) family of chromatin remodeling proteins in the pathobiology of cancer is fairly well recognized, the physiological role of MTA proteins continues to be an understudied research area and is just beginning to be recognized. Similar to cancer cells, MTA1 also modulates the expression of target genes in normal cells either by acting as a corepressor or coactivator. In addition, physiological functions of MTA proteins are likely to be influenced by its differential expression, subcellular localization, and regulation by upstream modulators and extracellular signals. This review summarizes our current understanding of the physiological functions of the MTA proteins in model systems. In particular, we highlight recent advances of the role MTA proteins play in the brain, eye, circadian rhythm, mammary gland biology, spermatogenesis, liver, immunomodulation and inflammation, cellular radio-sensitivity, and hematopoiesis and differentiation. Based on the growth of knowledge regarding the exciting new facets of the MTA family of proteins in biology and medicine, we speculate that the next burst of findings in this field may reveal further molecular regulatory insights of non-redundant functions of MTA coregulators in the normal physiology as well as in pathological conditions outside cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Toh Y, Pencil SD, Nicolson GL. A novel candidate metastasis-associated gene, mta1, differentially expressed in highly metastatic mammary adenocarcinoma cell lines. cDNA cloning, expression, and protein analyses. J Biological Chemistry. 1994;269(37):22958–22963. - PubMed
-
- Toh Y, Pencil SD, Nicolson GL. Analysis of the complete sequence of the novel metastasis-associated candidate gene, mta1, differentially expressed in mammary adenocarcinoma and breast cancer cell lines. Gene. 1995;159(1):97–104. - PubMed
-
- Mazumdar A, Wang RA, Mishra SK, Adam L, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Mandal M, et al. Transcriptional repression of oestrogen receptor by metastasis-associated protein 1 corepressor. Nature Cell Biology. 2001;3(1):30–37. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Ma L, Zhao J, Liu X, Li Z, Zhang Y. Expression profile of MTA1 in adult mouse tissues. Tissue Cell. 2009;41(6):390–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

