A novel calcium-dependent mechanism of acquired resistance to IGF-1 receptor inhibition in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 25344862
- PMCID: PMC4253414
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2346
A novel calcium-dependent mechanism of acquired resistance to IGF-1 receptor inhibition in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
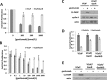
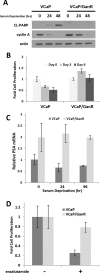
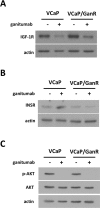
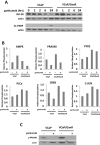
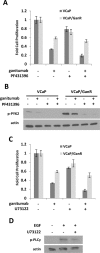
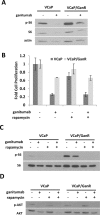
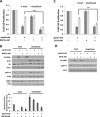
Inhibition of the mitogenic insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling axis is a compelling treatment strategy for prostate cancer. Combining the IGF-1R inhibitor ganitumab (formerly AMG 479) with standard of care androgen-deprivation therapy greatly delays prostate cancer recurrence in xenograft models; however, a significant proportion of these tumors ultimately acquire resistance to ganitumab. Here we describe the development of a stable and reproducible ganitumab-resistant VCaP human prostate cancer cell derivative termed VCaP/GanR to investigate the mechanism of acquired resistance to IGF-1R inhibition. Unlike parental VCaP, VCaP/GanR did not undergo apoptosis following ganitumab treatment. VCaP/GanR did not express increased levels of IGF-1R, insulin receptor, or phospho-AKT compared to parental VCaP. VCaP/GanR exhibited increased levels of phospho-S6 indicative of increased mTOR activity. However, acquired resistance to ganitumab was not dependent on increased mTOR activity in VCaP/GanR. Phospho-proteomic arrays revealed alterations in several calcium-regulated signaling components in VCaP/GanR compared to VCaP. Reduction of intracellular calcium using cell-permeable calcium-specific chelators restored ganitumab sensitivity to VCaP/GanR through inhibition of cell-cycle progression. These data suggest a new mechanism of resistance to IGF-1R inhibition involving calcium-mediated proliferation effects. Such pathways should be considered in future clinical studies of IGF-1R inhibitors in prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Pedro J. Beltran is an employee of and owns stock in Amgen, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62(1):10–29. - PubMed
-
- Breuhahn K, Longerich T, Schirmacher P. Dysregulation of growth factor signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2006;25(27):3787–3800. - PubMed
-
- Beltran PJ, Chung YA, Moody G, Mitchell P, Cajulis E, Vonderfecht S, Kendall R, Radinsky R, Calzone FJ. Efficacy of ganitumab (AMG 479), alone and in combination with rapamycin, in Ewing's and osteogenic sarcoma models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;337(3):644–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

