Methylation of miR-129-5p CpG island modulates multi-drug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting ABC transporters
- PMID: 25344911
- PMCID: PMC4294356
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2594
Methylation of miR-129-5p CpG island modulates multi-drug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting ABC transporters
Abstract
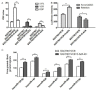
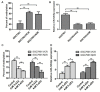
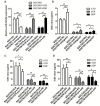
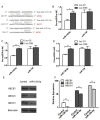
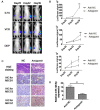
Recent studies have reported that hyper-methylation in the promoter region of miRNAs could silence the expression of tumor suppressive miRNAs and might play significant roles in the process of tumor development. However, the potential mechanisms regarding how methylation of miRNA CpG Island could regulate cancer cell chemo-resistance have not yet been studied. Using microarray and BSP (Bisulfate Sequencing PCR) assays, we found that compared with the parent SGC7901/VCR cells, expression of miR-129-5p was restored in SGC7901/VCR gastric cancer multi-drug resistant cell line treated by de-methylation reagent (5-AZA-dC). Using gain or loss of function assays, we found the over-expressed miR-129-5p reduced the chemo-resistance of SGC7901/VCR and SGC7901/ADR cells, while down-regulation of miR-129-5p had an opposite effect. Furthermore, three members of multi-drug resistance (MDR) related ABC transporters (ABCB1, ABCC5 and ABCG1) were found to be direct targets of miR-129-5p using bioinformatics analysis and report gene assays. The present study indicated that hyper-methylation of miR-129-5p CpG island might play important roles in the development of gastric cancer chemo-resistance by targeting MDR related ABC transporters and might be used as a potential therapeutic target in preventing the chemo-resistance of gastric cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rosmarinic acid reduces the resistance of gastric carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil by downregulating FOXO4-targeting miR-6785-5p.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:2327-2334. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.061. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551491
-
miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2008 Jul 15;123(2):372-379. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23501. Int J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18449891
-
AP-2α reverses vincristine-induced multidrug resistance of SGC7901 gastric cancer cells by inhibiting the Notch pathway.Apoptosis. 2017 Jul;22(7):933-941. doi: 10.1007/s10495-017-1379-x. Apoptosis. 2017. PMID: 28439677
-
Mouse ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters Conferring Multi-Drug Resistance.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(4):423-32. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25929575 Review.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in ABC transporters regulation and their clinical implications of multidrug resistance in cancer.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021 Mar;17(3):291-306. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2021.1887139. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33544643 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the mechanisms and challenges of cancer drug resistance.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 12;22(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01302-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38347575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-129-5p is regulated by choline availability and controls EGF receptor synthesis and neurogenesis in the cerebral cortex.FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3601-3612. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801094RR. Epub 2018 Dec 6. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30521373 Free PMC article.
-
Functional significance of cholesterol metabolism in cancer: from threat to treatment.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Sep;55(9):1982-1995. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01079-w. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37653037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ABC Transporters and Their Role in the Neoadjuvant Treatment of Esophageal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 15;19(3):868. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030868. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29543757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROR1 Expression and Its Functional Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Cells. 2019 Mar 2;8(3):210. doi: 10.3390/cells8030210. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30832318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Wagner KW, Alam H, Dhar SS, Giri U, Li N, Wei Y, Giri D, Cascone T, Kim JH, Ye Y, Multani AS, Chan CH, Erez B, Saigal B, Chung J, Lin HK, et al. KDM2A promotes lung tumorigenesis by epigenetically enhancing ERK1/2 signaling. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2013;123(12):5231–5246. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

