Beta oscillations reveal ethnicity ingroup bias in sensorimotor resonance to pain of others
- PMID: 25344947
- PMCID: PMC4483561
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsu139
Beta oscillations reveal ethnicity ingroup bias in sensorimotor resonance to pain of others
Abstract
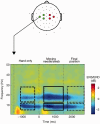
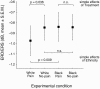
People evaluate members of their own social group more favorably and empathize more strongly with their ingroup members. Using electroencephalography (EEG), we explored whether resonant responses of sensorimotor cortex to the pain of others are modulated by the ethnicity of these others. White participants watched video clips of ethnic ingroup and outgroup hands, being either penetrated by a needle syringe or touched by a cotton swab, while EEG was recorded. Time-frequency analysis was applied to Laplacian-transformed signals from the sensors overlying sensorimotor cortex in order to assess event-related desynchronization and synchronization (ERD/ERS) of sensorimotor mu (7-12 Hz) and beta (13-30 Hz) rhythms. When watching needle injections, beta ERD was significantly stronger for ingroup compared with outgroup hands. This ethnicity bias was restricted to painful actions, as beta ERD for ingroup and outgroup hands neither differed when observing no-pain videos, nor during presentation of the hands without any treatment. Such vicarious sensorimotor activation could play a role in social interaction by enhancing the understanding of the feelings and reactions of others and hence facilitating behavioral coordination among group members.
Keywords: empathy; ingroup favoritism; mirror neurons; mu rhythm; racial bias.
© The Author (2014). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- AAPA. (1996). AAPA statement on biological aspects of race. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 101(4), 569–70.
-
- Allport GW. The Nature of Prejudice. Reading, MA.: Addison-Wesley; 1954.
-
- Avenanti A, Bueti D, Galati G, Aglioti SM. Transcranial magnetic stimulation highlights the sensorimotor side of empathy for pain. Nature Neuroscience. 2005;8(7):955–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

