Medical planning for mass-participation running events: a 3-year review of a half-marathon in Singapore
- PMID: 25345356
- PMCID: PMC4232663
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1109
Medical planning for mass-participation running events: a 3-year review of a half-marathon in Singapore
Abstract
Background: Systematically planning appropriate medical coverage for mass-participation running events is a challenge that has received relatively little attention in the medical literature, despite its potentially severe consequences. In particular, the literature lacks quantitative information on running events that medical planners can utilize for decisions on medical resource allocation and deployment.
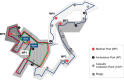
Methods: Using a case-study approach, this study provides a detailed quantitative medical services utilization profile for the Singapore Army Half-Marathon, constructed from participant and casualty data spanning three years and comprising over 80,000 data points. Casualty rates for participants of varying age and sex in different running events were also estimated using a multivariate logistic regression model. Qualitatively, planning processes and practices were described and discussed.
Results: The quantitative profile yielded three main findings. Firstly, the analysis reveals that the gross Medical Usage Rate had remained fairly stable at between 16.9 and 26.0 casualties per 10,000 participants over the three years. Secondly, comparing injury types, musculoskeletal and soft-tissue injuries were the most commonly-presented injuries. Thirdly, more casualties presented at the race end-point as compared to the along the race routes. The regression analysis showed that, of the four modeled variables, the longer event distance (21 km vs. 10 km) had the largest effect on the likelihood that a participant would become a casualty. Conversely, being of an older age, being male, and running in a non-competitive event were each associated with lower casualty risk.
Conclusions: The stable and intuitive casualty patterns detailed in this study provide a strong basis for further quantitative research on the medical aspects of running events, as well as for mass-participation sporting events in general. The qualitative aspects of this report may serve as a useful resource to medical planners for running events.
Figures



References
-
- Schexnayder CJ: The Marathon – more popular than ever. Stride Nation. http://www.stridenation.com/2012/2/28/2830407/the-marathon-more-popular-.... Accessed 5 May 13
-
- Running USA: 2013 Annual Half-Marathon Report. http://www.runningusa.org/index.cfm?fuseaction=news.details&ArticleId=33.... Accessed May 5 2013
-
- Lim Teck Yin: Opening Remarks at: Standard Chartered Marathon Singapore 2012 Press Conference, Oct. 29, 2012. Singapore; http://www.sportsingapore.gov.sg/newsroom/speeches/2012/10/opening-remar.... Accessed May 5 2013
-
- Grieshaber K, Augstein F: Germany Love Parade 2010 Tragedy: Death Toll Rises After Stampede at Festival. The Huffington Post. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2010/07/24/germany-love-parade-trage_n_658.... Accessed May 5 2013
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/14/1109/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

