Study on the Relationships between Intrinsic Functional Connectivity of the Default Mode Network and Transient Epileptic Activity
- PMID: 25346721
- PMCID: PMC4193009
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2014.00201
Study on the Relationships between Intrinsic Functional Connectivity of the Default Mode Network and Transient Epileptic Activity
Abstract
Rationale: Simultaneous recording of electroencephalogram and functional MRI (EEG-fMRI) is a powerful tool for localizing epileptic networks via the detection of hemodynamic changes correlated with interictal epileptic discharges (IEDs). fMRI can be used to study the long-lasting effect of epileptic activity by assessing stationary functional connectivity during the resting-state period [especially, the connectivity of the default mode network (DMN)]. Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) and idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) are associated with low responsiveness and disruption of DMN activity. A dynamic functional connectivity approach might enable us to determine the effect of IEDs on DMN connectivity and to better understand the correlation between DMN connectivity changes and altered consciousness.
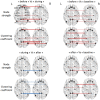
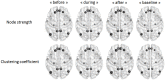
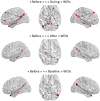
Method: We studied dynamic changes in DMN intrinsic connectivity and their relation to IEDs. Six IGE patients (with generalized spike and slow-waves) and 6 TLE patients (with unilateral left temporal spikes) were included. Functional connectivity before, during, and after IEDs was estimated using a sliding window approach and compared with the baseline period.
Results: No dependence on window size was observed. The baseline DMN connectivity was decreased in the left hemisphere (ipsilateral to the epileptic focus) in TLEs and was less strong but remained bilateral in IGEs. We observed an overall increase in DMN intrinsic connectivity prior to the onset of IEDs in both IGEs and TLEs. After IEDs in TLEs, we found that DMN connectivity increased before it returned to baseline values. Most of the DMN regions with increased connectivity before and after IEDs were lateralized to the left hemisphere in TLE (i.e., ipsilateral to the epileptic focus).
Conclusion: RESULTS suggest that DMN connectivity may facilitate IED generation and may be affected at the time of the IED. However, these results need to be confirmed in a larger independent cohort.
Keywords: default mode network; dynamic; epileptic interictal event; functional connectivity; idiopathic generalized epilepsy; posterior cingulate gyrus; precuneus; temporal lobe epilepsy.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Negative BOLD in default-mode structures measured with EEG-MREG is larger in temporal than extra-temporal epileptic spikes.Front Neurosci. 2014 Nov 18;8:335. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00335. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25477775 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time effects of interictal spikes on hippocampus and amygdala functional connectivity in unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy: An EEG-fMRI study.Epilepsia. 2019 Feb;60(2):246-254. doi: 10.1111/epi.14646. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Epilepsia. 2019. PMID: 30653664
-
Increased Intrinsic Connectivity of the Default Mode Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Evidence from Resting-State MEG Recordings.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 2;10(6):e0128787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128787. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26035750 Free PMC article.
-
Voxel-wise Functional Connectivity of the Default Mode Network in Epilepsies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(1):254-266. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210325130624. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33823767 Free PMC article.
-
The structural and functional connectivity of the posterior cingulate cortex: comparison between deterministic and probabilistic tractography for the investigation of structure-function relationships.Neuroimage. 2014 Nov 15;102 Pt 1:118-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.022. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24365673 Review.
Cited by
-
Interictal Epileptiform Discharges Might Be More Likely During Particular Phases of Brain Activity.Front Neurol. 2015 Dec 4;6:253. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00253. eCollection 2015. Front Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26696954 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Multimodal imaging of dynamic functional connectivity.Front Neurol. 2015 Feb 16;6:10. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00010. eCollection 2015. Front Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25762977 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of the Default Mode Network (DMN) in Neurological and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Review.Yale J Biol Med. 2016 Mar 24;89(1):49-57. eCollection 2016 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27505016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain network dynamics in the human articulatory loop.Clin Neurophysiol. 2017 Aug;128(8):1473-1487. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 17. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28622530 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of fMRI and Wada tests in the presurgical evaluation of language functions in temporal lobe epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 30;13:884730. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.884730. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36247757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Binnie CD, Marston D. Cognitive correlates of interictal discharges. Epilepsia (1992) 33(Suppl 6):S11–7 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

