Endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates the cerebrovascular effects of erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 25346735
- PMCID: PMC4191322
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00494
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates the cerebrovascular effects of erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: Erythropoietin (Epo) improves post-traumatic cerebral blood flow (CBF), pressure autoregulation, and vascular reactivity to l-arginine. This study examines the dependence of these cerebral hemodynamic effects of Epo on nitric oxide generated by endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS).
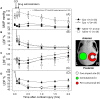
Methods: Using laser Doppler flow imaging, CBF was monitored in wild-type (WT) and eNOS-deficient mice undergoing controlled cortical impact followed by administration of Epo (5000 U/kg) or normal saline.
Results: Cerebral blood flow decreased in all groups post-injury with the greatest reductions occurring at the impact site. Epo administration resulted in significantly higher CBF in the peri-contusional sites in the WT mice [70.2 ± 3.35% in Epo-treated compared to 53 ± 3.3% of baseline in saline-treated mice (p < 0.0001)], but no effect was seen in the eNOS-deficient mice. No CBF differences were found at the core impact site where CBF dropped to 20-25% of baseline in all groups.
Conclusion: These differences between eNOS-deficient and WT mice indicate that the Epo mediated improvement in CBF in traumatic brain injury is eNOS dependent.
Keywords: cerebral blood flow; erythropoietin; neuroprotection; nitric oxide; nitric oxide synthase; traumatic brain injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the cerebral hemodynamics after controlled cortical impact injury in mice.J Neurotrauma. 2003 Oct;20(10):995-1006. doi: 10.1089/089771503770195849. J Neurotrauma. 2003. PMID: 14588116
-
Neuroprotection with erythropoietin administration following controlled cortical impact injury in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Aug;322(2):789-94. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.119628. Epub 2007 Apr 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17470644
-
Relative contributions from neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthases to regional cerebral blood flow changes during forebrain ischemia in rats.Neuroreport. 2000 May 15;11(7):1549-53. Neuroreport. 2000. PMID: 10841375
-
Involvement of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Cerebral Microcirculation and Oxygenation in Traumatic Brain Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1395:3-7. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14190-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36527605 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: a potential therapeutic target for cerebrovascular diseases.Mol Brain. 2016 Mar 22;9:30. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0211-9. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27000187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Erythropoietin in Optic Neuropathies: Current Future Strategies for Optic Nerve Protection and Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 27;23(13):7143. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137143. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythropoietin Attenuates the Brain Edema Response after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2018 Feb 15;35(4):671-680. doi: 10.1089/neu.2017.5015. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Neurotrauma. 2018. PMID: 29179621 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin and its derivatives: from tissue protection to immune regulation.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Feb 3;11(2):79. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2276-8. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32015330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Erythropoietin on Phenylhydrazine-Induced Hemolytic Hyperbilirubinemia in Neonatal Rats.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):1026-1037. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2135-2. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27995496
-
The Effect of Erythropoietin and Its Derivatives on Ischemic Stroke Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 17;13:743926. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.743926. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35250554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coronado VG, Xu L, Basavaraju SV, McGuire LC, Wald MM, Faul MD, et al. Surveillance for traumatic brain injury-related deaths – United States, 1997-2007. MMWR Surveill Summ (2011) 60(5):1–32 - PubMed
-
- Gorio A, Gokmen N, Erbayraktar S, Yilmaz O, Madaschi L, Cichetti C, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin counteracts secondary injury and markedly enhances neurological recovery from experimental spinal cord trauma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2002) 99:9450–510.1073/pnas.142287899 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

