Meiotic behavior of 18 species from eight families of terrestrial heteroptera
- PMID: 25347839
- PMCID: PMC5443580
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/ieu011
Meiotic behavior of 18 species from eight families of terrestrial heteroptera
Abstract
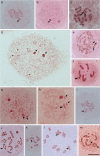
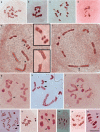
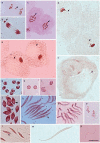
Insects of the suborder Heteroptera are known for their odor, for being pests, or for being disease carriers. To gain better insight into the cytogenetic characteristics of heteropterans, 18 species of terrestrial Heteroptera belonging to eight families were studied. The presence of heteropycnotic corpuscles during prophase I, terminal or interstitial chiasmas, telomeric associations between chromosomes, ring disposals of autosomes during metaphase, and late migrations of the sex chromosomes during anaphase were analyzed. These features showed identical patterns to other species of Heteroptera previously described in the literature. Another studied characteristic was chromosome complements. The male chromosome complements observed were 2n = 12 chromosomes [10A + XY, Galgupha sidae (Amyot & Serville) (Corimelaenidae) and Pachycoris torridus (Scopoli) (Scutelleridae)]; 2n = 13 [10A + 2m + X0, Harmostes serratus (Fabricius), Harmostes apicatus (Stål), Jadera haematoloma (Herrich-Schaeffer), Jadera sanguinolenta (Fabricius), Jadera sp. (Rhopalidae)], and Neomegalotomus parvus (Westwood) (Alydidae); 2n = 13 [12A + X0, Stenocoris furcifera (Westwood) (Alydidae); 2n = 14 [12A + XY, Dictyla monotropidia (Stål) (Tingidae)]; 2n = 19 [18A + X0, Acanonicus hahni (Stål) (Coreidae)]; 2n = 21 [18A + 2m + X0, Acanthocephala sp. (Dallas) (Coreidae)]; 2n = 27 [24A + 2m + X0, Anisoscelis foliacea marginella (Dallas) (Coreidae)]; 2n = 18 [16A + XY, Oncopeltus fasciatus (Dallas) (Lygaeidae)]; 2n = 17 [14A + X1X2Y, Oxycarenus hyalinipennis (Costa) (Lygaeidae)]; 2n = 16 [12A + 2m + XY, Pachybrachius bilobatus (Say) (Lygaeidae)]; 2n = 26 [24A + XY, Atopozelus opsinus (Elkins) (Reduviidae)]; and 2n = 27 [24A + X1X2Y, Doldina carinulata (Stål) (Reduviidae)]. The diversity of the cytogenetic characteristics of Heteroptera was reflected in the 18 studied species. Thus, this study extends the knowledge of these characteristics, such as the variations related to chromosome complements, sex chromosome systems, and meiotic behavior.
Keywords: chromosome; cytogenetic; holocentric; meiosis.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Entomological Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Description of the pre-reductional sex chromosome during male meiosis of Pachylis laticornis (Heteroptera: Coreidae).Genet Mol Res. 2016 Apr 28;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027592. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27173284
-
Meiosis, spermatogenesis and nucleolar behavior in the seminiferous tubules of Alydidae, Coreidae and Rhopalidae (Heteroptera) species.Genet Mol Res. 2009 Nov 17;8(4):1383-96. doi: 10.4238/vol8-4gmr672. Genet Mol Res. 2009. PMID: 19937583
-
Cytogenetics analysis and testis morphology of aquatic species of the families Belostomatidae, Gelastocoridae, Gerridae, Notonectidae, and Veliidae (Heteroptera).J Insect Sci. 2015 Mar 22;15(1):21. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iev009. Print 2015. J Insect Sci. 2015. PMID: 25797798 Free PMC article.
-
A checklist of chromosome numbers and a review of karyotype variation in Odonata of the world.Comp Cytogenet. 2020 Oct 22;14(4):501-540. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v14i4.57062. eCollection 2020. Comp Cytogenet. 2020. PMID: 33173570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inverted meiosis: the true bugs as a model to study.Genome Dyn. 2009;5:137-156. doi: 10.1159/000166639. Genome Dyn. 2009. PMID: 18948713 Review.
Cited by
-
A new species of the genus Rhaphidosoma Amyot et Serville, 1843 (Heteroptera, Reduviidae), with data on its chromosome complement.Comp Cytogenet. 2021 Dec 15;15(4):467-505. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v15.i4.78718. eCollection 2021. Comp Cytogenet. 2021. PMID: 35035781 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Chromosomal Evolution Understanding of Lygaeioid True Bugs (Lygaeoidea, Pentatomomorpha, Heteroptera) by Classical and Molecular Cytogenetic Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 15;14(3):725. doi: 10.3390/genes14030725. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bressa M. J., Papeschi A. G., Larramendy M. L. . 2001. . Meiotic studies in Largaeus alboornatus Blanchard (Heteroptera, Lygaeidae: Lygaeinae) . Caryologia 55 : 15 – 19 .
-
- Bressa M. J., Fumagalli E., Ituarte S., Frassa M. V., Larramendy M. L. . 2002. . Meiotic studies in Dysdercus Guérin Méneville 1831 (Heteroptera: Pyrrhocoridae). II. Evidence on variations of the diffuse stage between wild and laboratory-inbred populations of Dysdercus chaquency Freiberg, 1948 . Hereditas 137 : 125 – 131 . - PubMed
-
- Castanhole M. M., Pereira L. L., Souza H. V., Bicudo H. E., Costa L. A., Itoyama M. M. . 2008. . Heteropicnotic chromatin and nucleolar activity in meiosis and spermiogenesis of Limnogonus aduncus (Heteroptera, Gerridae): a stained nucleolar organizing region that can serve as a model for studying chromosome behavior . Genet. Mol. Res . 7 : 1398 – 1407 . - PubMed
-
- Castanhole M. M., Pereira L. L., Souza H. V., Itoyama M. M. . 2010. . Spermatogenesis and karyotypes of three species of water striders (Gerridae, Heteroptera) . Genet. Mol. Res . 9 : 1343 – 1356 . - PubMed
-
- Cattani M. V., Papeschi A. G. . 2004. . Nucleolus organizing regions and semi-persistent nucleolus during meiosis in Spartocera fusca (Thunberg) (Coreidae, Heteroptera) . Hereditas 140 : 105 – 111 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

