Acute cyclooxygenase inhibition does not alter muscle sympathetic nerve activity or forearm vasodilator responsiveness in lean and obese adults
- PMID: 25347862
- PMCID: PMC4187568
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12079
Acute cyclooxygenase inhibition does not alter muscle sympathetic nerve activity or forearm vasodilator responsiveness in lean and obese adults
Abstract
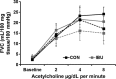
Obesity is often characterized by chronic inflammation that may contribute to increased cardiovascular risk via sympathoexcitation and decreased vasodilator responsiveness. We hypothesized that obese individuals would have greater indices of inflammation compared with lean controls, and that cyclooxygenase inhibition using ibuprofen would reduce muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) and increase forearm blood flow in these subjects. We measured MSNA, inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein [CRP] and Interleukin-6 [IL-6]), and forearm vasodilator responses to brachial artery acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside in 13 men and women (7 lean; 6 obese) on two separate study days: control (CON) and after 800 mg ibuprofen (IBU). CRP (1.7 ± 0.4 vs. 0.6 ± 0.3 mg/L; P < 0.05) and IL-6 (4.1 ± 1.5 vs. 1.0 ± 0.1pg/mL; P < 0.05) were higher in the obese group during CON and tended to decrease with IBU (IL-6: P < 0.05; CRP: P = 0.14). MSNA was not different between groups during CON (26 ± 4 bursts/100 heart beats (lean) versus 26 ± 4 bursts/100 heart beats (obese); P = 0.50) or IBU (25 ± 4 bursts/100 heart beats (lean) versus 30 ± 5 bursts/100 heart beats (obese); P = 0.25), and was not altered by IBU. Forearm vasodilator responses were unaffected by IBU in both groups. In summary, an acute dose of ibuprofen did not alter sympathetic nerve activity or forearm blood flow responses in healthy obese individuals, suggesting that the cyclooxygenase pathway is not a major contributor to these variables in this group.
Keywords: Autonomic nervous system; blood pressure; forearm blood flow; inflammation.
© 2014 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acute cyclooxygenase inhibition and baroreflex sensitivity in lean and obese adults.Clin Auton Res. 2017 Feb;27(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10286-016-0389-z. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Clin Auton Res. 2017. PMID: 27838779 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity and heart rate in patients with type 2 diabetes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):H1170-H1179. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00384.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27591221 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle sympathetic nerve activity and hemodynamic alterations in middle-aged obese women.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001 Apr;34(4):475-8. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2001000400006. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2001. PMID: 11285458
-
Adrenergic and reflex abnormalities in obesity-related hypertension.Hypertension. 2000 Oct;36(4):538-42. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.36.4.538. Hypertension. 2000. PMID: 11040232 Clinical Trial.
-
Abnormal neurovascular control during sympathoexcitation in obesity.Obes Res. 2003 Nov;11(11):1411-9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2003.190. Obes Res. 2003. PMID: 14627763
Cited by
-
Modulation of Aβ42 in vivo by γ-secretase modulator in primates and humans.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015 Aug 5;7(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0137-y. eCollection 2015. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26244059 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of resistance vessel function in human skeletal muscle: guidelines for experimental design, Doppler ultrasound, and pharmacology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):H301-H325. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00649.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31886718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association between sleep duration and muscle sympathetic nerve activity.Clin Auton Res. 2023 Dec;33(6):647-657. doi: 10.1007/s10286-023-00965-7. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Clin Auton Res. 2023. PMID: 37543558 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase attenuates the blood pressure response to plantar flexion exercise in peripheral arterial disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Aug 1;309(3):H523-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00267.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26055794 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrinological and Epigenetic Mechanisms Subserving Autonomic Imbalance and HPA Dysfunction in the Metabolic Syndrome.Front Neurosci. 2016 Apr 14;10:142. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00142. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27147943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez G. E., Beske S. D., Ballard T. P., Davy K. P. 2002. Sympathetic neural activation in visceral obesity. Circulation; 106:2533-2536. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez G. E., Ballard T. P., Beske S. D., Davy K. P. 2004. Subcutaneous obesity is not associated with sympathetic neural activation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol.; 287:H414-H418. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez G. E., Halliwill J. R., Ballard T. P., Beske S. D., Davy K. P. 2005. Sympathetic neural regulation in endurance‐trained humans: fitness vs. fatness. J. Appl. Physiol.; 98:498-502. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

